CONTENTS:
COVER STORY: Action on Social Audit Findings: Issues and Challenges
Hon’ble Governor of Telangana Dr. (Smt.) Tamilisai Soundararajan Attends NIRDPR Foundation Day as Chief Guest
NIRDPR Celebrates 74th Republic Day
NIRDPR Signs MoU with VAMNICOM
Three-day ToT on Effective Implementation of National Biodiversity Act through Panchayats
NIRDPR Officials attend Official Language Conference Held in Kerala
ToT on Capacity Building Programme on e-GramSwaraj Portal for PRI Functionaries
Mission Antyodaya Survey 2022 – NIRDPR Conducts Orientation Training for States/UTs
Training on Use of RS & GIS for Planning, Real-time Monitoring and Implementation of WDC PMKSY 2.0 Scheme
Webinar on Media and Rural Development: Forging Network for Rural Communication Interventions
Participatory Approaches and Technology Interventions for Rural Development through Unnat Bharath Abhiyan
COVER STORY:
Action on Social Audit Findings: Issues and Challenges
The Auditing Standards 2016, released by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) define social audit as, ‘An audit that is conducted by the people, by those who are affected by, or are the intended beneficiaries of the scheme being audited and facilitated by the Government.’ Social Audit is a means of achieving the twin goals of accountability and transparency through community participation. Section 17 of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) mandates the conduct of regular social audits by the Gram Sabha at least once every six months. MGNREGA guidelines, Audit of Scheme Rules, 2011 and Auditing Standards 2016 gave a detailed description regarding the establishment of a Social Audit Unit (SAU) to facilitate audits, process of social audit and the follow-up actions to be taken.
As on January 2023, all the States except Goa have established SAUs as a separate Society and these social audit units have been facilitating social audits and coming out with findings in the States. The process of social audit would be completed when action is taken on these findings. An analysis of findings and actions taken for the financial years 2017-18, 2018-19 and 2019-20 is given below, followed by the challenges being faced while taking action on social audit findings.
Findings of the Social Audit:
During the process of conducting social audits, findings are classified into four types – Grievance, Process Violation, Financial Deviation, and Financial Misappropriation. Under each finding, there are categories and sub-categories.
Issues Reported on the NREGA MIS for the FY 2017-18 to 2019-20:
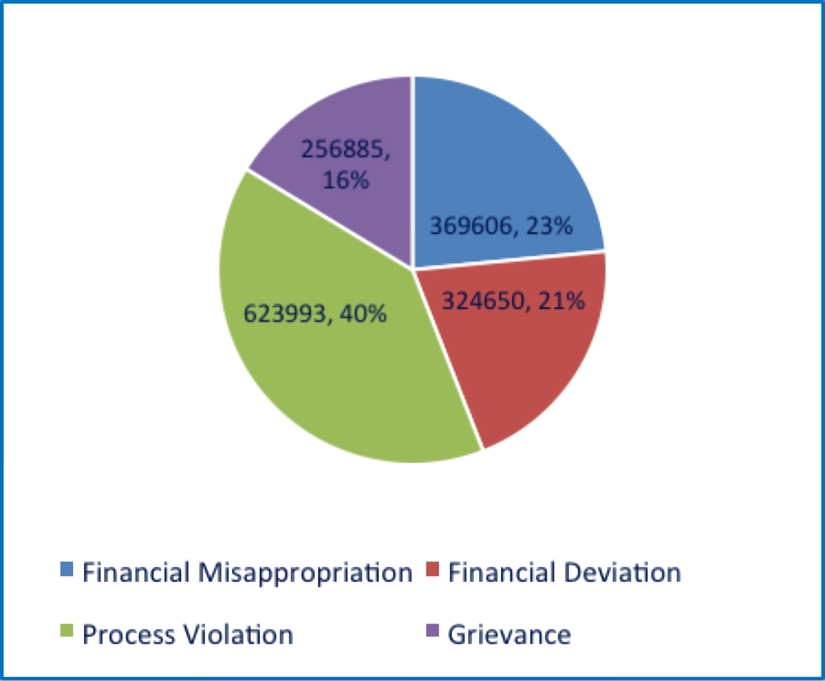
A total of 15, 75,134 issues were reported during the financial years 2017-18, 2018-19 and 2019-20. Among these, 40 per cent were related to process violation, 23 per cent were related to financial misappropriation, 21 per cent were related to financial deviation, and 16 per cent were related to grievances.
Financial Misappropriation Issues Reported Year-on-Year:
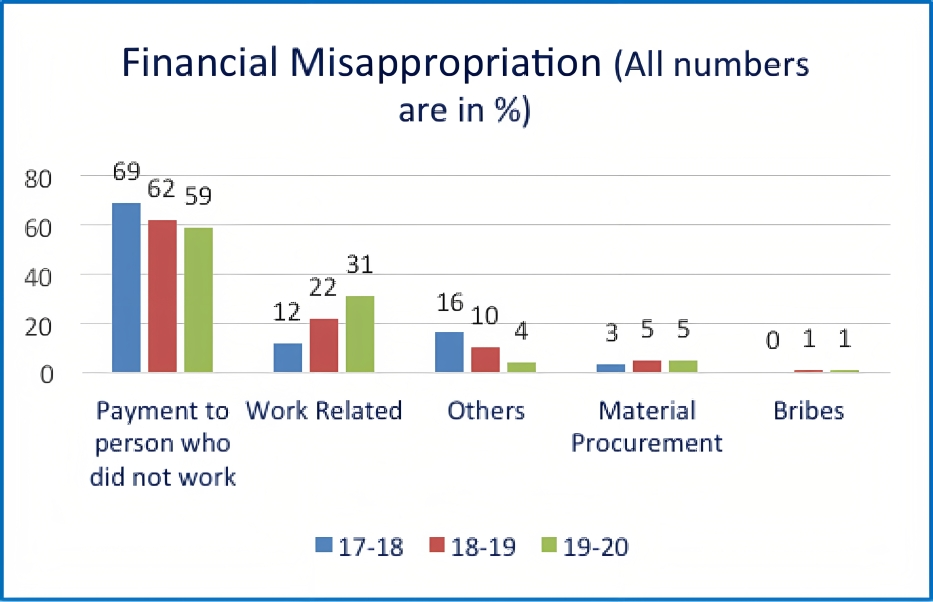
Five different categories are reported under financial misappropriation which can be seen from the graph. In the graph, payment to person who did not work was a major issue over the three financial years. The second largest issue was work-related, which increased from 12 per cent to 31 per cent from 17-18 to 19-20 FY. The percentage of the number of issues reported related to “Payment to the person who did not work”, and “Others” have declined over the years whereas “Wages related” and “Material procurement” have increased over the years. There is not much change in the bribes category, while 63 per cent of the financial misappropriation is related to the “Payment to the person who did not work” category.
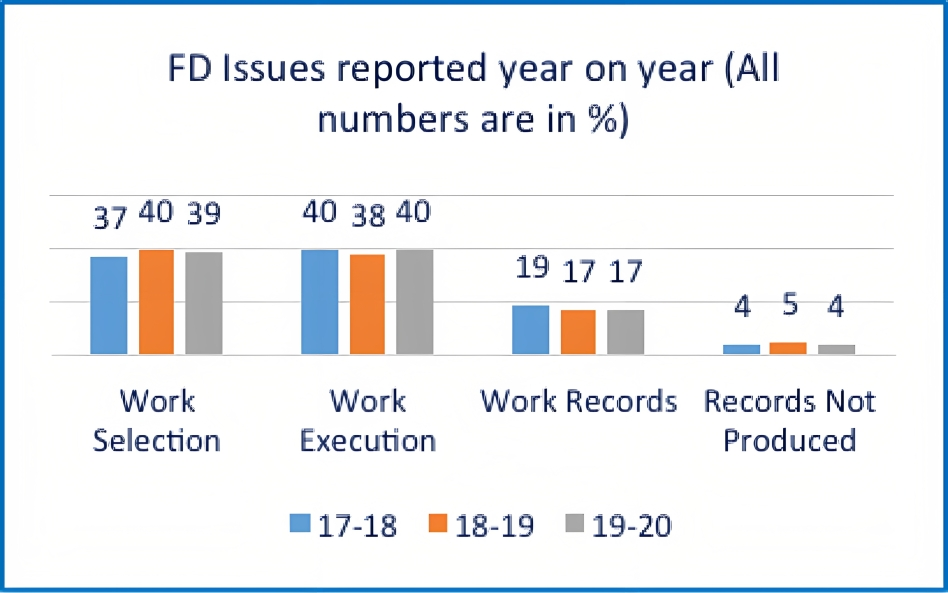
Financial Deviation Issues Reported Year-on-Year:
Most of the issues were reported under (almost 80 per cent over the three years) work selection and work execution categories only. The cases in the work selection category have increased in the 18-19 FY and have decreased by 1 per cent in the FY 19-20. Records pertaining to Rs. 280 crore were not submitted to the social audit team, which is a violation of the MGNREG Act.
Issues Related to Process Violation:
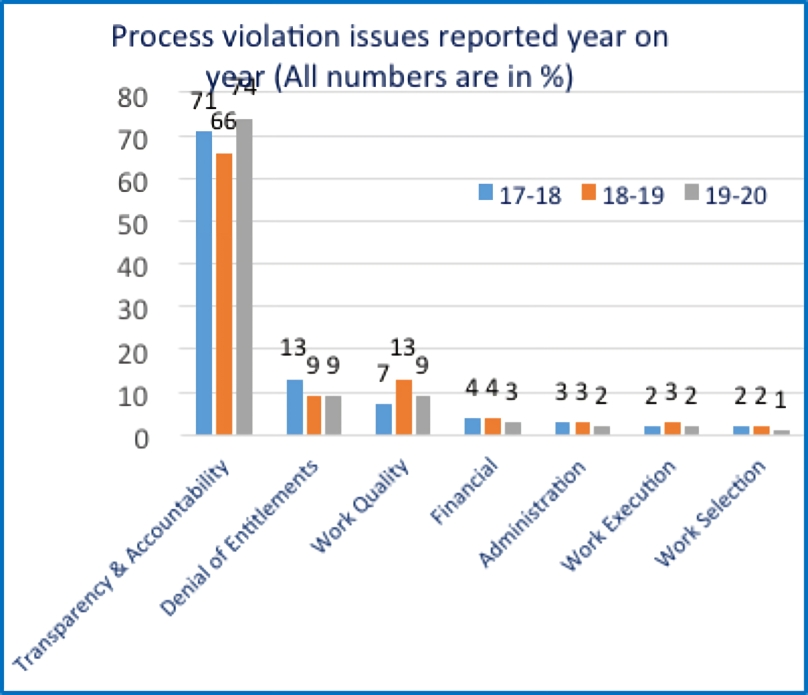
Transparency and accountability issues have decreased by 5 per cent in 18-19 and increased by 8 per cent in 19-20. About 70 per cent of the issues reported are related to transparency and accountability. Denial of entitlements decreased by 4 per cent in 2018-19 and remained the same in 19-20. The work quality-related issues saw an increase in 18-19, but it has come down in 19-20.
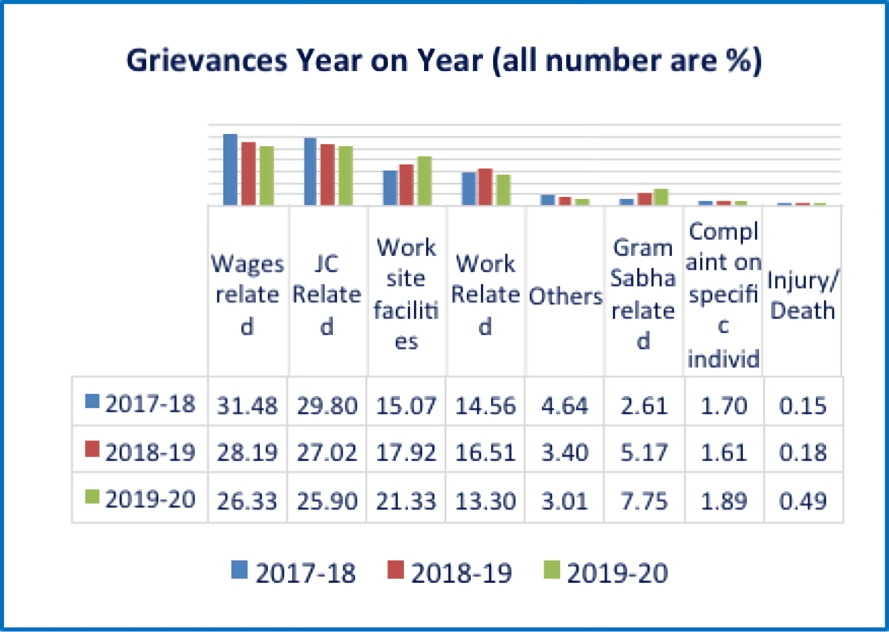
Issues Related to Grievances:
While wage-related and job card-related grievances declined over the years, worksite facilities and Gram Sabha-related grievances have increased over the years. Work-related grievances increased by 2 per cent in 18-19 but decreased by 3 per cent in 19-20. Most of the grievances are reported under wage-related, job card-related, worksite facilities and work-related categories. One of the major issues is the delay in payment of wages. On-time payment continues to be the greatest challenge as far as MGNREGS wage seekers are concerned. There is a need for a realistic solution to this issue, where by wage seekers know at what level their payments have been held up.
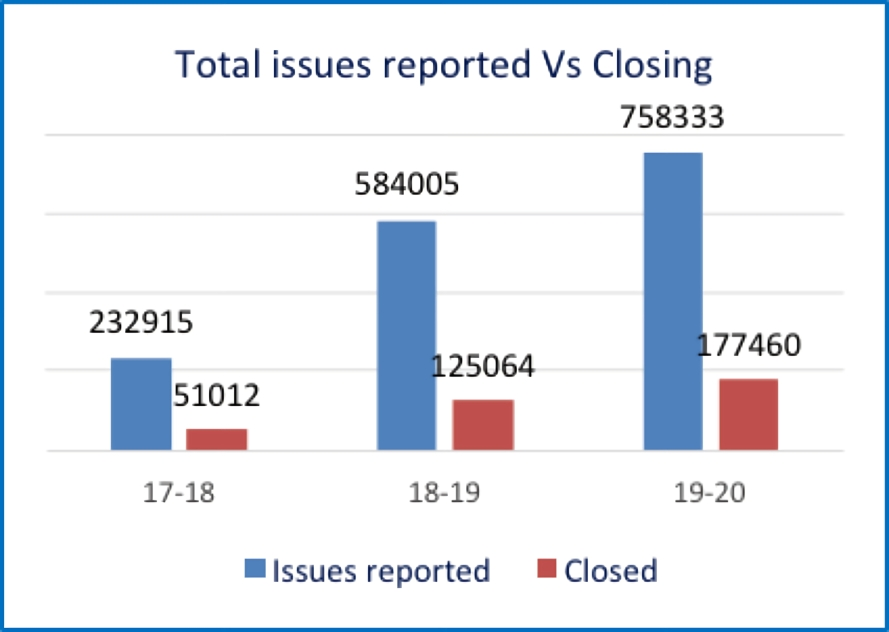
Action Taken on the Social Audit Findings:
All MGNREGA implementing officials in the States are mandated to take action on social audit findings and to enter it in the NREGA Soft. On June 22, 2018, the MoRD sent a letter to all States requesting them to respond to the action taken report for each social audit finding in the MIS itself within 30 days.
- While a total of 15,75,134 issues were reported during the FY 17-18, 18-19 and 19-20 only 3,53,536 issues (22 per cent) were closed.
- A total of 3,69,606 financial misappropriation issues were reported for the FY 17-18, 18-19 and 19-20 in which 60,287 issues were closed (16 per cent of the total cases reported). The closing percentage of the misappropriation issues is less compared to the overall closing.
State-wise Recovery Status
| S. No. | State | Recovery percentage | S. No | State | Recovery percentage |
| 1 | Tamil Nadu | 9.09 | 12 | Himachal Pradesh | 7.45 |
| 2 | Karnataka | 1.83 | 13 | West Bengal | 0.06 |
| 3 | Andhra Pradesh | 0.69 | 14 | Uttarakhand | 0.08 |
| 4 | Telangana | 1.38 | 15 | Maharashtra | 11.05 |
| 5 | Jharkhand | 0.62 | 16 | Nagaland | 0 |
| 6 | Chhattisgarh | 3.47 | 17 | Madhya Pradesh | 8.69 |
| 7 | Punjab | 0.7 | 18 | Sikkim | 47.95 |
| 8 | Uttar Pradesh | 0.29 | 19 | Mizoram | 3.95 |
| 9 | Bihar | 0 | 20 | Haryana | 0 |
| 10 | Tripura | 0 | 21 | Arunachal Pradesh | 20.11 |
| 11 | Odisha | 8.19 |
Regarding follow-up and actions of social audit findings, the Auditing Standards 2016 say:
- A follow-up mechanism should be established to monitor and ensure that action has been taken on the findings of the social audit
- Responsibilities and timelines should be assigned for corrective actions in a time-bound manner
The MGNREGS Annual Master Circular says ‘All States are mandated to arrange for a three-tier vigilance mechanism to proactively detect irregularities in the implementation of the Act and to follow up detected irregularities and malfeasance, including those identified during the social audit, and ensure that the guilty are punished and recoveries of misspent funds duly made.’
However, only Telangana and Andhra Pradesh created a Vigilance Cell to follow up on the social audit findings and ensure that adequate action is taken. Auditing Standards 2016 and Annual Master Circular also direct States to frame rules for action taken on social audit findings; however, till date only implementing agencies from Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Telangana and Uttarakhand have issued rules/GOs regarding the actions to be taken on the findings. Ministry should constitute an independent committee, comprising top officials, policy experts and experienced civil society representatives, to facilitate States for framing rules and establish mechanisms for proper action and closer of issues and irregularities identified through Social Audit.
Conclusion
If Social Audits, as intended, should empower citizens to ask questions and monitor government programmes from below, the process needs to create trust among the people for which timely and effective actions on findings of social audits are needed. The Government of India should issue an advisory for action on irregularities identified under MGNREGA. This will help the States to prepare their own advisory by including State-specific issues. For follow-up on the action taken on the issues identified, periodic reviews should be done at the district and State levels by the officials concerned.
There shall be hearings at GP, Block, District, State and national levels to resolve the issues identified during the social audit. Discussing issues only at block or district levels will not help in resolving all the issues as a few require intervention at the policy level. Social audit findings should be discussed at district-level bi-monthly review meetings and also at State level review meetings. There should be an independent body/committee at all levels to review the action taken by the implementing agency. Since the topics discussed are connected to the lives of the people, the participation of CSOs and wage labourers needs to be ensured in these committees. The MoRD should collect an action plan to strengthen social audits from each SAU and State, and it should follow up to ensure that the action plan is carried out during MTR, PRC and other such forums.
Dr. Srinivas Sajja (with inputs from the CSA team)
Assistant Professor, Centre for Social Audit
NIRDPR
Hon’ble Governor of Telangana Dr. (Smt.) Tamilisai Soundararajan Attends NIRDPR Foundation Day as Chief Guest
The National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR) celebrated its 64th Foundation Day on 20th January 2023. Hon’ble Governor of Telangana and Hon’ble Lt. Governor of Puducherry Dr. (Smt.) Tamilisai Soundararajan was the Chief Guest of the event held at Vikas Auditorium on the Institute premises.
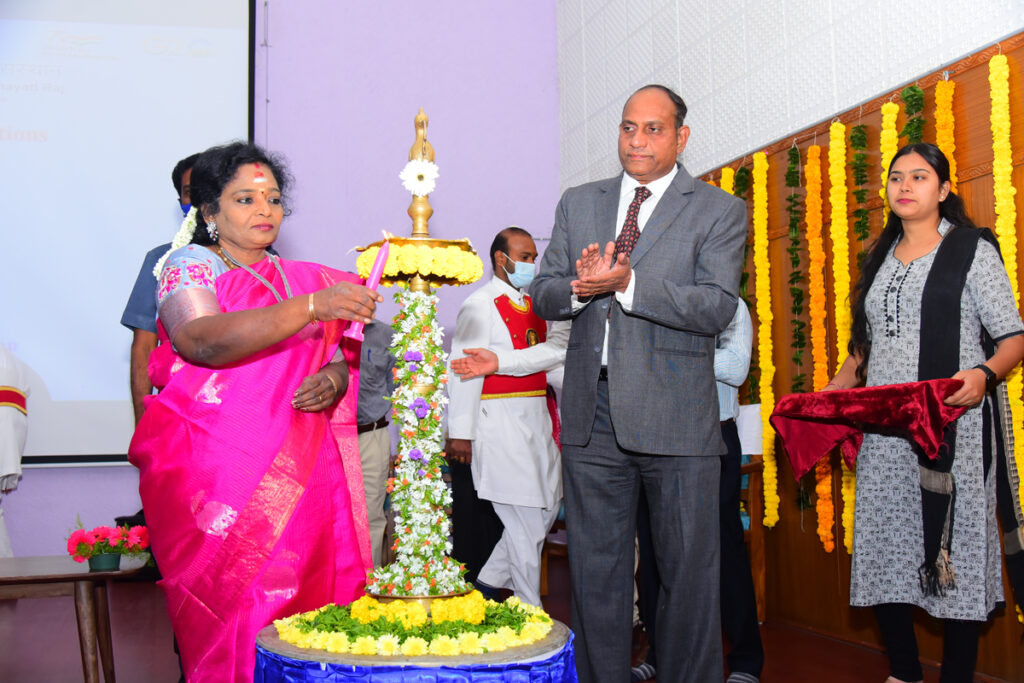

The Governor inaugurated the Foundation Day celebrations by lighting the lamp and delivered an address. “India lives in villages; it is vital for overall development to strengthen these Panchayati Raj Institutions, as envisioned by honourable Prime Minister of India Shri Narendra Modi. Rural India is witnessing transformational changes in road connectivity, internet connectivity, mobile service access, and digital payments. The rural areas are, in fact, competing with the urban areas, I strongly believe that rural development is a holistic process of economic, social and human development. As we march towards 2030, many targets set for sustainable goals have been achieved and are in progress. India has achieved benchmarks in many sectors like education and health and still, a lot needs to be done for the people belonging to marginal sectors,” she said.

Dr. (Smt.) Tamilisai Soundararajan expressed that NIRDPR has been encouraging rural artisans across the country by organising national-level melas and wanted such initiatives to be continued for the betterment of rural economy. She shared her personal experiences as a doctor while serving in the field, and noted that decentralising the powers, decentralising the development and focussing on rural development are needed for the development of the whole country.
“Article 243 H of the Constitution authorises the State to empower the local government to levy, collect and appropriate certain taxes, duties, tolls and etc. It is difficult for those in rural areas to understand tax issues. Rural development is also about creating awareness among the people. Government comes up with many programmes and schemes, but they should reach the needy,” she said.
The Governor said she was informed by Dr. Narendra Kumar, DG, NIRDPR, regarding the new initiative in which the population from the rural areas are trained by professionals to treat minor ailments in the peripheral areas.
“Connectivity is more important; if there is connectivity, fetching doctors in emergencies is easy. Sanitation is another area where more work has been done,” she said. Citing a study regarding the construction of toilets in rural schools bringing down the dropout rate, she encouraged NIRDPR to carry out research on these things and inform the government. Dr. (Smt.) Tamilisai Soundararajan further congratulated NIRDPR for celebrating the 64th Foundation Day and called the occasion an achievement.

Associate Professor & Head, CICT, NIRDPR (extreme right) are also seen.
Earlier, Shri M. Srikanth, Registrar (Administration), NIRDPR delivered the welcome address, and Dr. G. Narendra Kumar, IAS, Director General, NIRDPR gave the opening remarks.
Welcoming Dr. (Smt.) Tamilisai Soundararajan on the occasion of the 64th Foundation Day celebrations of NIRDPR, the Director General said the Institute is at the forefront of rural development. “We serve as an apex training body with 29 SIRDs (State Rural Development Institutes) and 90 ETCs (Extension Training Centres). NIRDPR has had several achievements working as a think tank. The recent initiatives have been a focused development of training calendar. NIRDPR is the foremost repository of social audit in the country and has been working with the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment,” he said.

“We have signed 20 MoUs with prestigious institutions to increase capabilities and are planning to enter into similar pacts. With the encouragement of Dr. (Smt.) Tamilisai Soundararajan, we organised a training programme for legal professionals on the PESA (Panchayats Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996. We organised a State Finance Commissioners Conclave and WASH conclave. Taking into consideration the 75 years of Independence and Azadi Ka Amrut Mahotsav, we are working on establishing a school of excellence on Panchayati Raj. Developing micro-enterprises for the self-help groups and promoting energy-sufficient villages are another focus areas. We are planning to conduct a State Election Commissioners Conclave and are also working on integrating agriculture planning with Gram Panchayat planning. We have organised 1300 training programmes and trained 60,000 PRI functionaries; this way, we have dedicated ourselves for the development of the nation,” the DG said.
On the occasion, Dr. (Smt.) Tamilisai Soundararajan released the book ‘Proceedings of National Conclave on State Finance Commissions.’ An MoU between NIRDPR and Gandhigram Rural Institute was also signed in her presence.
Later in the day, Dr. Narendra Kumar, IAS, Director General, NIRDPR, inaugurated the Nobel Laureate Corner established at the Library Building on the Institute premises.
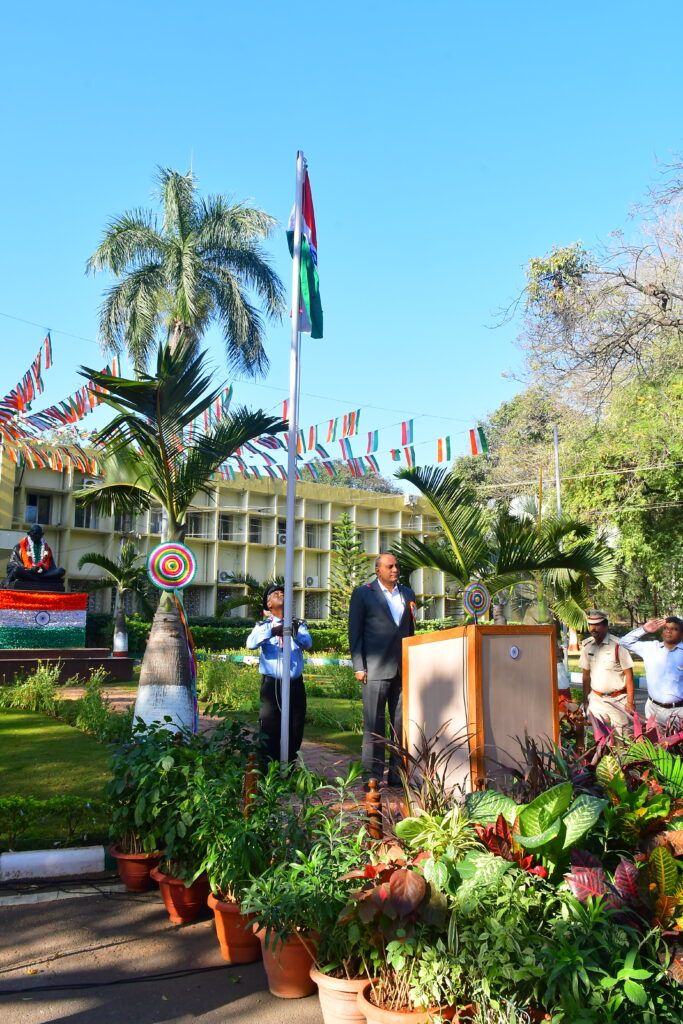
NIRDPR Celebrates 74th Republic Day
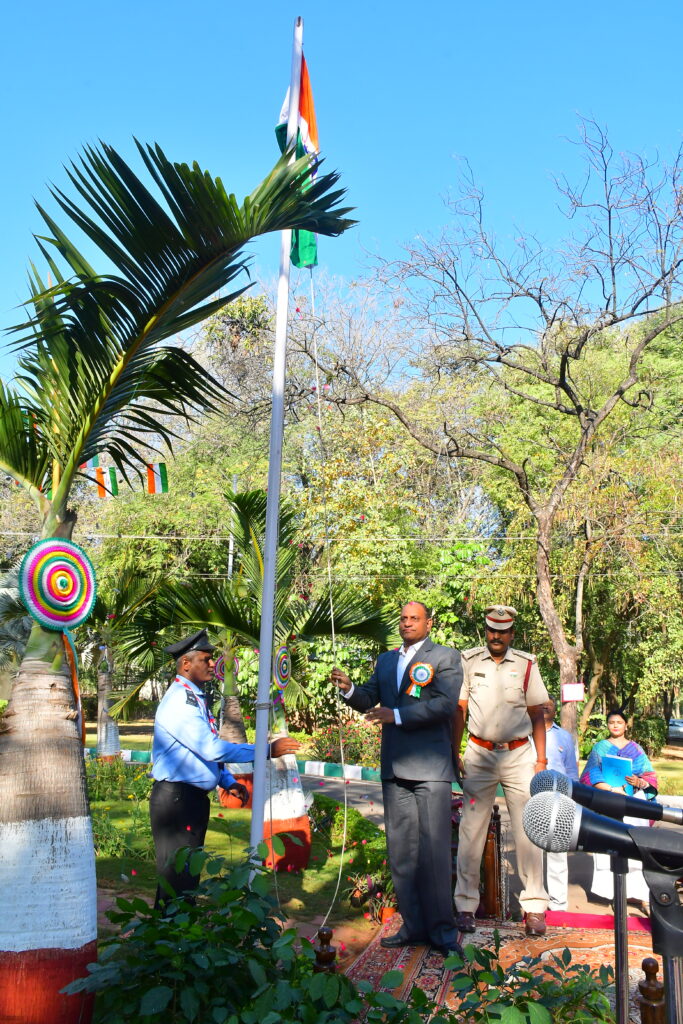

Dr. G. Narendra Kumar, IAS, Director General, NIRDPR, hoisting the national flag during the 74th Republic Day celebrations held at the Institute
The National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj celebrated 74th Republic Day on 26th January 2023. Dr. G. Narendra Kumar, IAS, Director General, NIRDPR was the Chief Guest of the event.
The Director General hoisted the national flag in front of the Mahatma Gandhi Block on the Institute premises. Greeting everyone on the occasion of Republic Day, the DG spoke about the role played by NIRDPR in the rural development sector.
“This is a day for us to recognise the contributions made by our faculty members to this Institute as well as national progress and development. During the occasion marking the 75th year of India’s independence, we reviewed the remarkable achievements of the country and NIRDPR’s contribution to those significant accomplishments. In the last 75 years, India has moved from the situation of having a begging bowl in its hand to the third largest exporter of agricultural produce in the world. At the stroke of Independence, about 80 per cent of India’s population was poor. The situation has been reversed now with 80 per cent of the population above the poverty line,” he pointed out.
“India has made significant progress and has become the fifth largest economy in the world going ahead of the United Kingdom, the long-time occupier of India. Before colonisation, India was the most prosperous economy in the world; today, it is the fifth largest economy in the world. If we continue to make progress as expected, India would become the fourth largest economy going beyond Germany by 2025, and by 2026 or so, we are expected to become the third largest economy going beyond Japan. This progress is being made by our country under the able leadership of our visionary Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi whose vision we should all align with,” he said.
“The government spends about three-and-a-half lakh crore rupees every year for the welfare of the poor, downtrodden and the disadvantaged. Among the latest studies, there is an extensive study on Adarsh Gram Express Yojana which provides transportation facilities on rural roads through self-help group enterprises. Through the network of SIRDs and Extension Training Centres, NIRDPR is reaching out to each and every Panchayat of the country, and that is the uniqueness of this Institute. Therefore, it becomes our greater responsibility to contribute to the progress of the country. NIRDPR has been signing Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) with so many reputed organisations. The Institute has also successfully conducted the State Finance Commissioners Conclave. Many activities related to Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Scheme and Jal Jeevan Mission are being carried out by the Institute. NIRDPR makes outstanding contributions to capacity building of rural development and panchayati raj functionaries in the country. NIRDPR’s works span the entire knowledge spectrum, which means we are creating knowledge to evidence-based research and applying that created knowledge through action research and the digital Knowledge from action research projects. While the self-sustenance of the Institute is a challenge, it can also be a great opportunity for us. With every challenge comes an opportunity and the opportunity here is one of greater freedom to do what we want to do to be better recognised,” the DG said and sought the support and cooperation of employees to develop NIRDPR into a vibrant Institute.
On the occasion, the staff serving in the Security section of the Institute took out a march past. The Director General and Shri Shashi Bhushan, DDG (i/c), distributed prizes to the winners of various sports and games competitions organised as part of the Republic Day celebrations. The event was attended by faculty members, non-academic staff and students.
PHOTO GALLERY
The video link of the event is provided below:
NIRDPR Signs MoU with VAMNICOM

The National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Vaikunth Mehta National Institute of Cooperative Management (VAMNICOM), Pune on 3rd January 2023 in presence of Dr. G. Narendra Kumar, IAS, Director General, NIRDPR and Dr. Hema Yadav, Director VAMINICOM, Pune.
This MoU is to further the collaboration in supporting and strengthening Panchayati Raj Institutions, Cooperative Organisations, including multi-State cooperatives societies and self-help groups.
Both the institutions agreed for organising capacity development training programmes in areas related to cooperative management for rural development and panchayati raj functionaries, and seminars and workshops on contemporary issues of cooperative management and rural development. Both institutes mutually agreed to work together to take forward the schemes and programmes of the Ministry of Cooperation, Government of India.
The institutes will also jointly undertake collaborative evidence-based research studies on cooperative management-related themes pertaining to rural India. Besides developing training modules for training, collaborative research and action research programmes and Training of Trainers (ToT) in the area of cooperative management and rural development will also be conducted. The faculty exchange for PG Programmes is one of the key components of the MoU.

Speaking on this occasion, Dr. G. Narendra Kumar, IAS, Director General, NIRDPR, mentioned the constitution of the core committee to prepare an action plan to take the MoU forward in conducting evidence-based research by the faculty members of both the institutes in the interest of cooperatives. He emphasised on the transformation of SHGs into micro-enterprises through the credit support of Primary Agricultural Cooperative Societies (PACS) in the country.
Dr. Hema Yadav, Director VAMINICOM, appreciated the initiatives taken by NIRDPR at the grassroots level and expressed that different technology applications used at NIRDPR would be useful for the faculty of VAMINICOM in taking forward the cooperative research.
On this occasion, a book title‘ ‘Inclusive Growth in Indian Agriculture: Need for Commercially Viable and Financially Sustainable FPs’ written by Dr. M. Srikanth, Registrar and Director (Administration), NIRDPR was released by Dr. Hema Yadav, Director, VAMINICOM. The book is based on a research study sponsored by the Centre for International Cooperation and Training in Agricultural Banking, VAMINICOM Pune.
Three-day ToT on Effective Implementation of National Biodiversity Act through Panchayats

A three-day Training of Trainers (ToT) on Effective Implementation of the National Biodiversity Act through Panchayats was conducted from 9th to 11th January 2023 by the Centre for Wage Employment & Livelihoods, National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj. The training programme covered topics, including Biodiversity & Good Quality of Life, Biodiversity Act 2002: Letters and Spirit and Biodiversity Management committees and Its Functions.
Biodiversity & Good Quality of Life
Prof. Jyothis Sathyapalan, Course Coordinator & Head of the Centre for Post Graduate Studies and Distance Education, delivered the welcome speech. This was followed by a detailed introduction of the training programme to the participants. He briefed them about the relevance and importance of the ‘National Biodiversity Act 2002’ at the Gram Panchayat level.
An objective test was conducted to evaluate the understanding of the participants about the National Biodiversity Act 2002. The first lecture was on ‘Biodiversity & Ecosystem Services and its Linkages with Good Quality of Life.’ Dr. Jyothis took the participants through the practical definition of biodiversity and spoke about all the kinds of biodiversity services that we enjoy without giving back the due credit to the nature we live in.
The second session focused on the ‘Linkages of Human Life with Biodiversity Conservation.’ The participants were given a practical exercise on various ‘Ecological Services’ that are consumed in their native places and a way forward to conserve the biodiversity of the native places/villages.
Biodiversity Act 2002: Letters and Spirit
The second day began with a session on understanding the National Biodiversity Act, 2002. Dr. Jyothis explained how in the absence of the National Biodiversity Act 2002, the indigenous knowledge from the tribes of the area concerned was getting exploited and how the Act talks about the importance of native tribes and their indigenous knowledge. He also elaborated on the gradual shift the Act has witnessed from conserving and preserving biodiversity to sustainable use of biodiversity. Dr. Jyothis highlighted the fact that during the latest COP 15 (Conference of the Parties 15) on biodiversity, the stakeholders acknowledged the fact that without any offer of incentive, natives don’t feel obliged enough to conserve biodiversity. “So, to make them naturally interested in the conservation of biodiversity, we must allow them some incentive,” he noted.

As a part of practical implementation, the participants prepared a list of the species of plants and animals, which were in abundance and are now reduced to just some rare sightings in their native places. While preparing the list, they were asked to also talk about the change in weather patterns (if any), changes in agricultural practices and the condition of land and water bodies near their native places. While talking about the problem, they were also encouraged to come up with practical solutions to restore the biodiversity/land condition loss that has happened in native places over the years.
Further, Dr. K. Jyothi, Scientist, Environment Protection Training & Research Institute (EPRI), Telangana gave a basic introduction to the National Biodiversity Act 2002, its significance and the relevance of indigenous knowledge for the effective implementation of the Act. She explained the structure of Biodiversity Management committees, and its functions and significance. After a brief touch-up on the need and significance of indigenous knowledge, while implementing the National Biodiversity Act 2002, she initiated the main conversation on ‘How to conduct a participatory Rural Appraisal for preparinPeople’s Biodiversity Register.’
Dr. K. Jyothi took the participants through the whole process of collecting relevant information from the indigenous people. “It involves all the documentation and formalities, but the main focus is to make the indigenous tribe trust you to build a mutual understanding with them so that they will not conceal any crucial fact while disseminating information about any particular herb, treatment or practice,” she said.
While talking about the process, Dr. K. Jyothi elaborated on the challenges that one faces while collecting the information. She duly advised the participants to not think of this process as a standard procedure. “Every time a group of officials set out to gather knowledge by following the norms, they have to make it a unique and personal experience for the tribe; only then, the end goal could be achieved,” she added.

Later, Ms. Salomi Yesudas, an ‘all-seasons’ resource person, took a session on the significance of ‘uncultivated food sources.’ She lectured on ‘Biodiversity Conservation, Food Security and Nutrition: The Case of Uncultivated Plants and Case Studies.’
Dr. Salomi began with a brief introduction on Uncultivated Foods and how can they single-handedly fulfil all our micro-nutrition needs on a daily basis. She took the class through various research-based data on the nutritional value of various uncultivated food items, which can forfeit the hunger crisis in the rural strata of the population. She further gave the participants a task to list out all the foods and vegetables available in their respective areas, the festivals and foods associated with them and the different food sources available in their native places. Later, the participants learnt about various food choices, options and preparation techniques available at various geographic locations in India. A post-training evaluation was conducted and Dr. Jyothis Sathyapalan, Course Coordinator delivered the valedictory address. The training was attended by officials of the Goa Biodiversity Board and Kerala Institute of Local Administration (KILA), representatives from Gram Panchayats in Maharashtra, and members of the Karnataka Biodiversity Board.
NIRDPR Officials Attend Official Language Conference Held in Kerala

The Rajbhasha Vibhag, Ministry of Home Affairs, New Delhi organised a one-day Joint Regional Official Language Conference for South and South-West Regions and Prize Distribution ceremony in Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala on 27th January 2023.
Officers/employees of various Central Government offices, including the Secretary and Joint Secretary of the Department of Official Language, Ministry of Home Affairs, attended the conference. Smt. Anita Pandey, Assistant Director (Official Language), National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR) and V. Annapurna, Junior Hindi Translator represented the Institute in the event held at Tagore Theatre in Thiruvananthapuram. Shri Arif Mohammad Khan, Hon’ble Governor of Kerala and Shri Ajay Kumar Mishra, Hon’ble Minister of State for Home Affairs, were the Chief Guests of the conference.
Addressing the audience, Shri Arif Mohammad Khan said the culture of India is rich and will always remain incredible. Reciting several slokas in Sanskrit, he said there is no competition between languages, and opined that one should feel proud of speaking in Hindi.
Shri Ajay Kumar Mishra, Hon’ble Minister of State, Ministry of Home Affairs observed that Hindi is easy to learn and is spoken by the common people. He mentioned that the Department of Official Language, Ministry of Home Affairs, is doing the implementation work of Hindi through Town Official Language Implementation Committees. “The Department of Official Language, Ministry of Home Affairs, works for the promotion of official language under the supervision of the Parliamentary Committee on Official Language. Kanthasth-2.0, a translation tool and Hindi Shabd Sindhu dictionary were launched by Hon’ble Home Minister at the Dwitiya Akhil Bhartiya Rajbhasha Sammelan held in Surat in September last year. Kanthasth-2.0 is a helpful tool for translation work. Similarly, the LILA-Rajbhasha application developed by the Department of Official Language helps learn Hindi through 14 regional languages,” he said.
Earlier, Smt. Anshuli Arya, Secretary, Department of Official Language welcomed the guests and gave detailed information about the promotion of Hindi in South India. Ms Meenakshi Jolly, Joint Secretary, Department of Official Language, Ministry of Home Affairs, proposed a vote of thanks.
ToT on Capacity Building Programme on e-GramSwaraj Portal for PRI Functionaries

The Centre for Good Governance and Policy Analysis (CGGPA) organised a series of offline and online Training of Trainers on ‘Capacity Building programme on e-GramSwaraj Portal for PRI Functionaries.’ The off-campus ToT programmes were organised at Andhra Pradesh from 12th -15th December 2022 at SIRDPR, Andhra Pradesh and from 27th -30th December 2022 at SIRDPR, Telangana sponsored by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj, Government of India. Two two-day national-level online training programmes were arranged from 20th -21st December 2022 and 22nd-23nd December 2022.
SIRDPR, Andhra Pradesh
A total of 39 participants, including State level Officials, DPMs, ADPMs, and district in-charges participated in this programme. The programme was inaugurated by Shri Selva Reddy, Joint Director (Admn.) and Shri Doshi Reddy, Joint Director. In the inaugural speech, they highlighted the importance of uploading Gram Panchayat Development Plan in the GPDP and eGramSwaraj portals. They also emphasised on the latest developments in planning the GPDP with a special focus on the inclusion of SDG themes while planning the activities of Gram Panchayat.
SIRDPR, Telangana
In total, 29 participants comprising MPDOs and MPPs participated in the four-day ToT programme. The programme was inaugurated by Shri Anil Kumar, Joint Director. Shri Srikanth, Joint Director acted as the training coordinator from SIRD and highlighted the significance of eGramSwaraj Portal and coverage of the SDG themes in GPDP.
Online Training Programmes
Two two-day online training programmes were organised from 20th -21st December 2022 and 22nd -23rd December 2022. The first batch had 75 participants whereas 65 participants attended in the second batch and they were faculty, Project Managers, DPMs, ADPMs and Programmers from Madhya Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Ladakh, Uttarakhand, Andhra Pradesh and Odisha.
The offline and online training programmes were aimed at building skills and knowledge on the latest developments of e- GramSwaraj Portal.
In addition to this, the ToT covered sessions on Panchayat profile, planning module integration with Sankalp Se Siddhi scheme in the vibrant Gram Sabha, progress and financial reporting highlighting the significance of PFMS on 15 FC grants and Gram Manchitra with a focus on planning. All the sessions were demonstrated, and a hands-on training session was conducted in the demo portal.

Participatory learning methods were used to deliver the training. The sessions were dynamic and included introductory presentations, interactive sessions, lectures, documentary presentations, brainstorming and practical exercises, hands-on training, etc.
The participants opined that the programme design, contents, programme deliveries and hospitality arrangements were impressive. All four training programmes were coordinated by Shri K. Rajeshwar, Assistant Professor, Centre for Good Governance and Policy Analysis (CGGPA), NIRDPR.
Mission Antyodaya Survey 2022 – NIRDPR Conducts Orientation Training for States/UTs
Mission Antyodaya (MA) is a convergence and accountability framework launched by the Ministry of Rural Development in the year 2017, aiming to bring optimum use and management of resources allocated by 27 Ministries/Departments of the Government of India under various programmes for the development of rural areas. An annual survey in Gram Panchayats across the country is an important aspect of the Mission Antyodaya framework. It is carried out coterminous with the People’s Plan Campaign (PPC) of the Ministry of Panchayat Raj, and its purpose is to lend support to the process of participatory planning for the Gram Panchayat Development Plan (GPDP). The primary objective of Mission Antyodaya is to survey and collect village infrastructure and services data for nearly 600,000 villages in the country. The data collected from the villages are aggregated to rank GPs, and this process has been undertaken annually since 2017.
In 2017, when the Mission was launched, the baseline survey was conducted in selected 5,000 clusters encompassing 44,125 Gram Panchayats (GPs). The survey was extended to all the remaining GPs (around 2.2. lakh) in the entire country in 2018, and the GP ranking was repeated. During the 2019 phase, all the GPs were covered using a revised questionnaire which included an additional set of questions to ensure better policy coherence to achieve the objective of sustainable development. During FY 19-20, more than 2.6 lakh Gram Panchayats and 6 lakh villages were covered under the Mission Antyodaya survey. The survey was carried out in over 7000 blocks spread across 715 districts of all States and UTs except Delhi and Chandigarh.
In 2020, all the GPs were enumerated using the same questionnaire of 2019. The previous data available for the village, i.e., Census 2011 or MA 2017, 2018, or 2019 was used as baseline data which was updated and digitised by Gram Sevaks as Mission Antyodaya 2020 data with the help of an Android mobile application. The Gram Panchayats, where the data was already collected in the previous phases of the survey, were considered for data updation during this phase.
In 2021-22, no survey was done due to COVID-19 Pandemic. After a two-year break, MA Survey 2022 is to be undertaken from 9th February 2023. For the 2022 version of the survey, the questionnaire has been expanded to cover 216 Indicators, including 36 Indicators related to Gram Panchayat-level infrastructure and services. The rest of the indicators are related to village-level infrastructure and services.
NIRDPR has been closely associated with MoRD since the first survey launched in 2017, by orienting stakeholders on the survey process, providing value addition to the survey questionnaire and making the questionnaire and Android App available in regional languages.
NIRDPR organised four online training programmes on the 4th, 12th, 25th and 27th of January 2023, orienting about 480 participants, comprising State Nodal Officers, State Level Master Trainers and District Level Master Trainers from all States and UTs. The participants were trained on revamped Mission Antyodaya Questionnaire 2022 and MA Survey App. Resource persons from the Development Intelligence Unit (DIU) and NIC-MoRD supported NIRDPR in completing these orientation training programmes. A live demo of the MA App was organised, and the participants were oriented on the registration and full cycle of the survey process. The training programmes for all four batches were coordinated by Dr. C. Kathiresan, Associate Professor & Head (Nodal Officer for MA Survey 2022) and Dr. Venkatamallu Thadaboina, Research Officer, CRTCN, NIRDPR. Shri Arpan Hazra, Project Associate, CIATSJ, provided technical support in the MA App demonstration and required online support.
Dr. Venkatamallu Thadaboina, Research Officer
Dr. C. Kathiresan, Associate Professor & Head, CRTCN, NIRDPR
Training on Use of RS & GIS for Planning, Real-time Monitoring and Implementation of WDC PMKSY 2.0 Scheme

The Centre for Geoinformatics Applications in Rural Development (CGARD) organised a three-day training programme on ‘Use of RS & GIS for planning, real-time monitoring and implementation of WDC PMKSY 2.0 scheme’ sponsored by the Department of Land Resources (DoLR), Ministry of Rural Development from 2nd – 4th February 2023 at the State Institute of Rural Development & Panchayati Raj (SIRD&PR) Tamil Nadu.
Dr. M. V. Ravibabu, Associate Professor & Head (i/c), CICT, NIRDPR and Programme Director, inaugurated the programme and emphasised the use of Geo-Spatial Technology and its potential application in watershed planning, monitoring and management. He stressed that training of functionaries is a critical aspect that helps to keep them updated on the latest technological advancement, and the use of GIS-based technology would help to improve the standard of governance with utmost transparency and strengthened & authenticated through GIS tools, can enhance the planning of interventions in the best manner.
Dr. M. V. Ravibabu elaborated on the three-day programme schedule and objectives, such as Concepts of Geoinformatics, mobile applications for asset mapping of a watershed, and analysing of the GIS data layers for planning and the preparation of watershed plan, the operational guideline of WDC-PMKSY 2.0 objectives, deliverables, key deadlines, etc.

Smt. Seetha Lakshmi, Faculty of SIRD&PR, TN and local coordinator of the programme, outlined the key points of using GIS-based tools in spatial planning using Bhuvan Services and hands-on practical approach with field data collection from using mobile-based applications. In total, 21 PMKSY functionaries, including JE, AE, etc., attended the training. Dr. S. Devanayaki, Director, SIRD&PR and Smt. Kavitha, Executive Engineer of Rural Development, interacted with participants during the training programme.
The programme consisted of field visits for data collection using mobile GPS. All participants were divided into multiple teams to collect data on various assets. While collecting data from the field, participants experienced the field conditions and geo-tagging accuracy aspects.
On the last day, the course team from NIRDPR collected feedback from the participants and distributed certificates. Smt. Seetha Lakshmi, the local coordinator, expressed their gratitude to NIRDPR. The programme was a success, as per the feedback received from the participants. All participants felt that the training programme was helpful in preparing their DPRs using spatial tools.
Dr. M. V. Ravibabu, Associate Professor & Head (i/c), CICT
Shri Kiran Singh, Project Trainee, CGARD
Webinar on Media and Rural Development: Forging Network for Rural Communication Interventions
The National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj organised a webinar on ‘Media and Rural Development: Forging Network for Rural Communication Interventions’, on 24th January 2023.
Dr. Akanksha Shukla, Associate Professor, Centre for Post Graduate Studies & Distance Education, NIRDPR coordinated the programme. The speakers included Ms. Nidhi Jamwal, Managing Editor, Gaon Connection, Shri Gangadhar Patil, Founder, 101Reporters.com, Mr. Richard Mahapatra, Managing Editor, Down to Earth, Shri Arvind Shukla, Founder, News Potli, Shri Jaideep Hardikar and Shri People’sam Thakur from PARI (People’s Achieves of Rural India) and Mr. Mohd Irfan e Azam, Senior Journalist, Dainik Jagaran, representing the second largest Press Club of India at Siliguri, West Bengal.
The objective of the programme was to initiate a discussion on establishing a network of rural reporters under the aegis of NIRDPR to share news related to 29 subject areas under rural development for mutual benefit and people’s welfare.
Initiating the discussion, Shri Gangadhar Patil, Founder of 101Reporters.com wanted the rural journalists to be trained, incentivised and hand-held till a point where they do not require further assistance. “We need an informal group of rural reporters who would work together, with the freedom to pick stories which help more people to sign up for reporting rural issues. Especially, training them is more important than sitting them with every article. The sub-editing costs are high, but there have been people, who after their training are doing well for themselves now,” he said.
Mr. Richard Mahapatra, Managing Editor, Down to Earth, stressed on the need to form a rural reporters network. “In the past, there was mofussil journalism, and it was the core of reporting at the media organisations. Reporting is happening at the rural level, but it is no more regarding panchayati raj or keeping a watch on how the fund allocated to the village has been spent. It has become the most globalised reporting now – be it the development of India or climate change,” he observed.
“The network of reporters working on rural issues is required because it gives you a platform, and at the same time, the opportunity to get the required training. It can help you understand the basic issues that need to be highlighted and teach you how to find stories from Panchayats. This network can help the reporters find space for the stories, assist with issue briefing and offer support at a time when reporting is becoming an expensive affair,” he added.
Ms. Nidhi Jamwal, Managing Editor, Gaon Connection, said there is a need for training the journalists and making them work efficiently. “Moreover after training them, there should be a platform where they can publish their stories with bylines. The stories can be in print, audio or video format, but giving them a platform is more important,” she said and mentioned the new initiative of Gaon Radio to reach out to the people who cannot read.
Shri Arvind Shukla, Founder, News Potli observed that immense work is going on in the villages. “I have worked with rural women and trained them as Patrakar Didis. We have worked with teachers and school children for a long period by adding them to the team. Why should the district, tehsil and village reporters report the rural events? They should be trained in identifying issues and given proper pay and recognition for their work,” he said.
Shri Jaideep Hardikar, PARI (People’s Achieves of Rural India) outlined the challenges faced by the rural journalism sector, including lack of space from mainstream media, and funding of journalism. There is networking among journalists and organisations already in terms of learning and using the skill sets. There is a decline in reporting rural issues in the mainstream media. NIRDPR should take the lead and inform the journalists on various government initiatives and give briefs on the issues.
Shri Purusottam Thakur from PARI (People’s Achieves of Rural India) noted that the training, incentive and providing a platform have been long pending issues for development reporting. “Even the existing platforms for news are also coming down. There has been a rise in the number of YouTube channels and news portals. There have been other initiatives like video volunteers where women were trained, and they did bring out good articles,” he said.
Mr. Mohd Irfan e Azam, Senior Journalist, Dainik Jagaran, opined that the discussion is a good initiative from the side of NIRDPR. “The training part is being overemphasised. These days everyone possesses a smartphone and is using it vibrantly. Likewise, rural youth are using personal Facebook profiles and YouTube channels to get solutions to their issues. Rural journalism has become hyper-local, especially in places like Siliguri and northern parts of Bengal. Here are news portals from Paras or Mohallas. Platforms are not an issue; the main issue is the reach. Digital platforms will be a great thing to share information. At times, only the native resident of the village can understand the issue better than a seasoned journalist,” he said.
Appreciating NIRDPR forsaking up the initiative, the speakers further put forward the ways and approaches to be taken to take this initiative forward to the next level. The participants of this online programme also gave their opinions and shared their experiences. Dr. Akanksha Shukla proposed a vote of thanks.
Participatory Approaches and Technology Interventions for Rural Development through Unnat Bharath Abhiyan
A two-day training programme on Participatory Approaches and Technology Interventions for Rural Development through UBA was organised at the National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj from 7th -8th December 2022. This programme was sponsored by the Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, Ministry of Education, Government of India. In all, 17 faculty members from the State of Telangana attended this residential training programme. The objectives of this programme were
(1) To orient the participants about Unnat Bharat Abhiyan and its framework,
(2) To acquaint the participants with participatory approaches for rural development and proposal,
(3) To sharpen the skills in proposal writing under UBA,
(4) To acquaint the participants with the Localisation of Sustainable Development Goals,
(5) To illustrate the examples of convergence strategies, and
(6) To demonstrate appropriate technology interventions for rural development.
The programme was inaugurated by Prof. V. K. Vijay, National Coordinator, UBA, IIT, New Delhi. He emphasised the importance of UBA activities for holistic rural development. While interacting with all the participants, he enquired about the plethora of activities planned by them and the mode of execution. Prof. V. K. Vijay also guided the coordinators with ideas regarding the UBA activities and motivated them to take up the scheme extensively.
Dr. Lakhan Singh, Assistant Prof., Centre for Human Resource Development welcomed the participants. Eminent subject matter specialists were invited to interact with the participants on relevant and important topics, such as Participatory Approaches and Tools for Rural Development, Learning Loss due to the COVID-19 Pandemic, Preparation of the Village Development Plan under Unnat Bharath Abhiyan (UBA) using Gram Panchayat Development Framework, Localisation of Sustainable Development Goals in UBA, SAGY: A Model of Convergence-based Development, Appropriate Technologies for Rural Development, How to Write Effective Proposal under UBA, Samagra Gram Seva: An Initiative by IIT, Hyderabad, etc.
The participants from Participating Institutes (PIs) were asked to make a brief presentation on the activities undertaken by them focusing on the generation of resources and also to talk about the Action Plan. The participants were taken on a brief visit to the Rural Technology Park (RTP) located on the Institute premises wherein they had the opportunity of learning the appropriate technologies showcased. The programme was organised and coordinated by Dr. Lakhan Singh and Dr. R. Ramesh, Faculty Members of NIRDPR, Hyderabad. The participants complimented the course team for organising the training by covering all necessary inputs required to implement UBA activities effectively.







