
CONTENTS:
LEAD STORY: PM Vishwakarma Scheme: A Ray of Hope for Artisans
NIRDPR Celebrates 65th Foundation Day
Online Workshop on Linking CSR with Panchayati Raj (Local Governance) – A Roadmap for Strengthening Private Sector Work in Public Welfare
5-Day ToT on Agri-Startup/Agri-Entrepreneurship
Capacity Building of PRIs for Strengthening Community Health Care with a Focus on LSDG Theme 2: Healthy Village
Capacity Building and Experience Sharing Workshop on Community Adaptability and Sustenance Mechanisms at the Intersectionality of Water and Climate Change
Observance of Vigilance Awareness Week – 2023 at NIRDPR
Writeshop on Development of Training Module on Health under the Aspirational Block Development Programme
NIRDPR Delhi Branch Organises a Series of Workshops at SARAS Aajeevika Mela in Gurugram
LEAD STORY:
PM Vishwakarma Scheme: A Ray of Hope for Artisans
Ms Anushka Dwivedi &
Ms Ashna Vishwakarma
PGDM-RM Batch V Students, NIRDPR, Hyderabad
anushkadwivedi0422@gmail.com; ashnavishwa@gmail.com
India is a land of rich cultural heritage, and its handicrafts are a testament to this heritage. Artisans play a significant role in India’s cultural heritage and economy, contributing to the preservation of traditional crafts and generating employment opportunities. Indian artisans have been creating beautiful and intricate handicrafts for centuries, using a variety of traditional techniques. These handicrafts are not only aesthetically pleasing but also have a deep cultural significance which can be used effectively to utilise their skills and generate good livelihood opportunities for them.
There are 68.86 lakh artisans in India, of which 30.25 lakh (56.13 per cent) are males and 38.61 lakh are females (43.87 per cent). Of them, 20.8 per cent belong to Scheduled Castes, 7.5 per cent to Scheduled Tribes, 52.4 per cent to Other Backward Castes, whereas 19.2 per cent fall in General category.
The handicraft sector in India is unorganised and faces a number of challenges, including low capital, poor exposure to new technologies, absence of market intelligence, and a poor institutional framework. These challenges have hindered the growth of the sector. The Government of India has implemented various initiatives to support artisans, including provision of training, access to credit, and marketing assistance. However, more needs to be done to address the constraints faced by the sector and to promote its development.
Artisans are often confined to local markets and fairs, restricting their reach to a wider consumer base. Due to their geographical isolation and lack of exposure to modern marketing techniques, they struggle to connect with potential buyers in urban areas and international markets. Artisans often lack the knowledge and resources to effectively brand and market their products. They struggle to create a strong brand identity and reach potential customers through digital marketing channels.
The government schemes in India play a crucial role in uplifting and empowering artisans across various sectors. The Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI) and the Coir Board focus on revitalising traditional industries, providing financial aid, and fostering rural entrepreneurship. The National Handloom Development Programme (NHDP) and Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Hastkala Sankul Yojana contribute to the growth of handloom weavers and handicraft clusters by offering support in infrastructure, design innovation, and marketing. Aajeevika – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM) empowers artisans through skill development, capacity building, and access to credit. The Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) provides collateral-free loans, including support for micro-enterprises in the handicraft and artisan sectors. Initiatives like the National Bamboo Mission (NBM), Handicrafts and Artisans Comprehensive Welfare Scheme, Vanya Prani Mitra, and North East Region Textile Promotion Scheme (NERTPS) further contribute to the sustainable development of specific sectors, offering health insurance, skill enhancement, and market linkages. Together, these schemes aim to enhance the livelihoods of artisans, preserve traditional crafts, and foster economic growth in diverse regions of the country.
Due to cultural differences, administrative obstacles, administrative bureaucracy, lack of awareness, and geographic restrictions, craftsmen in India face difficulty accessing formal institutions. Many craftsmen, especially those working in isolated locations, find it difficult to get into these organisations, thereby losing opportunities for seeking financial aid and achieving professional growth. In order to overcome these obstacles and ensure equitable economic development, focused awareness efforts, streamlined application procedures, and use of technology are required. These will make formal institutions more accessible and advantageous for all craftspeople.
Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi introduced PM Vishwakarma, a Central Sector Scheme, on 17th September 2023, with the goal of offering comprehensive assistance to artisans and other craftspeople who use tools and their hands. The Programme includes craftspeople and artisans working in 18 different trades, such as Carpenter (Suthar/Badhai), Boat Maker, Armourer, Blacksmith (Lohar), Hammer and Tool Kit Maker, Locksmith, Goldsmith (Sonar), Potter (Kumhaar), Sculptor (Moortikar, stone carver), Stonebreaker, Cobbler (Charmkar)/ Shoesmith/Footwear artisan, Mason (Rajmistri), Basket/Mat/Broom Maker/Coir Weaver, Doll & Toy Maker (Traditional), Barber (Naai), Garland maker (Malakaar), Washerman (Dhobi), Tailor (Darzi) and Fishing Net Maker.
About the PM Vishwakarma Scheme

The scheme aims to support traditional craftsmen and artisans working in a variety of fields, such as carpentry, ceramics, blacksmithing, goldsmithing, and sculpting, with an emphasis on cultural heritage preservation and integration into formal economies and global value chains. Artisans and craftspeople, who are engaged in the 18 trades, are mentioned in the guidelines.
It will be carried out as a Central Sector Programme, entirely financed by the Government of India. Along with the Nodal Ministry, i.e. Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MoMSME), the scheme will be jointly implemented by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship and the Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
Eligibility: An artisan or craftsperson working with hands and tools in one of the foregoing family-based traditional trades in the unorganised sector on a self-employment basis is eligible for PM Vishwakarma registration. The minimum age of the beneficiary should be 18 years on the date of registration.
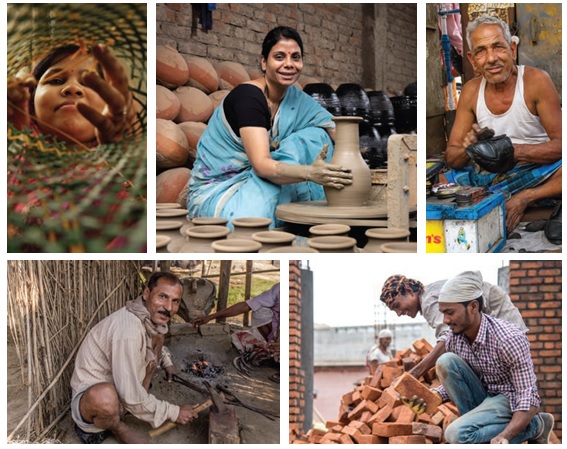

The PM Vishwakarma Yojana stands out as a comprehensive and innovative initiative designed to uplift artisans and craftspeople across India. One of its distinctive features is the issuance of a PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card, providing formal recognition to the skilled individuals in the artisan community. The scheme prioritises skill upgradation with a dual-tiered training approach—Basic Training of 5-7 days and Advanced Training of 15 days or more, by offering a stipend of Rs. 500 per day. A notable aspect is the toolkit incentive, where artisans receive e-vouchers of up to Rs. 15,000 at the commencement of basic skill training, which empowers them with the necessary tools for their craft.
The master training for the PM Vishwakarma Scheme commenced in Guhawati, Assam, on 17th November 2023, and 65 master trainers from six different states, namely Assam, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Tripura and Odisha, will be trained.
Theory of Change
| Domain of change | Indicators of changes | Outcomes (Short-term and Long-Term) |
| Recognition and Identity | Number of Vishwakarma Certificates and ID Cards distributed to artisans. | Improved recognition of artisans as Vishwakarmas and their integration into the economy. |
| Skills Enhancement | Number of artisans who undergo skill assessment and training. | Enhanced skills and capabilities of artisans, leading to increased income and market competitiveness. |
| Access to Modern Tools | Quantity of modern tools distributed to artisans. | Improved productivity, product quality, and economic upliftment for artisans. |
| Digital Empowerment | Number of digital transactions facilitated. | Increased efficiency and financial inclusivity among artisans through digital transactions. |
| Market Linkages | Number of artisans who receive marketing support. | Enhanced market competitiveness, brand promotion, and access to new opportunities for growth. |
| Formalisation of Informal Sector | Integration of traditional artisan activities into the formal economy. | Reduced economic disparities and social inclusion among marginalised groups. |
| Cultural Preservation | Preservation of cultural heritage and generational knowledge. | Continued practice of traditional crafts and generational knowledge transfer. |
| Increased Financial Security | Improved access to social security schemes. | Enhanced financial security and protection for artisans. |
| Market Competitiveness | Sustainable economic growth in the craft sector. | Sustainable income growth, economic upliftment, and employment generation. |
The PM Vishwakarma Yojana is a comprehensive initiative designed to bring immediate outputs and broader, long-term outcomes for artisans. The distribution of Vishwakarma certificates and ID cards aims to provide recognition and identity, thereby integrating artisans into the economy. The focus on skills enhancement through assessments and training contributes to increased capabilities, income, and market competitiveness. Providing modern tools enhances productivity and economic upliftment, while digital empowerment facilitates efficiency and financial inclusivity through digital transactions. Market linkages and marketing support promote competitiveness and growth opportunities. By formalising the informal sector and preserving cultural heritage, the scheme reduces economic disparities and ensures the transfer of generational knowledge. Improved access to social security schemes enhances financial security, ultimately fostering sustainable economic growth in the craft sector, leading to increased income, economic upliftment, and employment generation for artisans.
Challenges Faced During the Implementation of the Schemes and Its Expansion
The government has taken several initiatives, including the establishment of a dedicated portal for the PM Vishwakarma Scheme, conducting awareness campaigns about the scheme, providing training to trainers, developing market linkages for traditional handicrafts and products, and providing financial assistance to artisans and craftspeople.
Despite these efforts, the PM Vishwakarma Scheme faces a number of hurdles in the way of implementation. Difficulties in identifying and reaching out to traditional artisans and craftspeople, lack of awareness about the scheme among artisans and craftspeople, inadequate coordination between government agencies and NGOs involved in the implementation of the scheme, lack of adequate training infrastructure and facilities, inadequate availability of skilled trainers, difficulties in tailoring training programmes to meet the specific needs of different artisans and craft communities, lack of recognition for traditional skills and knowledge, difficulties in accessing markets for traditional handicrafts and products, strong competition from mass-produced low-cost products, lack of branding and marketing support for traditional handicrafts and products, and difficulties in ensuring the sustainability of businesses run by artisans and craftspeople are posing challenges. Therefore, constant monitoring and evaluation of the scheme to identify and address any emerging challenges is of paramount importance.
(The authors are grateful to Dr P. P. Sahu, Associate Professor, NIRDPR, for the initial discussion and suggestions on an earlier draft of the paper.)
NIRDPR Celebrates 65th Foundation Day
The National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj celebrated its 65th Foundation Day on 21st November 2023.
Shri Shailesh Kumar Singh, IAS, Secretary, Ministry of Rural Development, Government of India, was the Chief Guest of the celebrations held at Vikas Auditorium on the Institute campus. The dignitaries lighted the lamp, and Dr C. Kathiresan, Associate Professor& Head, CRTCN, delivered the welcome address.

Further, Shri Shailesh Kumar Singh, IAS, Secretary, Ministry of Rural Development released ‘Research Highlights 2022-23’ published by the Institute.
In his Foundation Day address, Shri Shailesh Kumar Singh said the occasion not only marks the anniversary of the organization’s establishment but also serves as a testament to the collective efforts, dedication, and resilience of each and every staff member.

“On this occasion, I appreciate the efforts of NIRDPR in meeting the capacity building requirements of the entire country for effectively implementing the rural development programmes. Rural development in India is a dynamic process that requires continuous adaptation to evolving challenges. Prospects for rural development are vast, with the potential to transform rural landscapes into vibrant and self-sufficient hubs. A holistic and integrated implementation approach, addressing economic, social, and environmental dimensions, is essential for sustainable rural development in India. Capacity building for such a programme implementation approach in rural development is crucial for fostering sustainable and inclusive growth in rural areas, which is necessary not only to enable the country to grow at an accelerated pace but also for us to move towards ‘Viksit Bharat’,” he said.
“Ministry of Rural Development acts as a nodal Ministry for most of the development and welfare activities in rural areas. Recognising the importance of capacity building, the MoRD through NIRDPR, is able to meet the requirements, as NIRDPR has a repository of knowledge on rural development, committed faculty and suitable infrastructure. I am glad that NIRDPR acts as a ‘think-tank’ for the Ministry of Rural Development by assisting the Ministry in policy formulation and by providing support to improve the implementation of ongoing rural development programmes that usher in the change,” the Secretary added.

Dr G. Narendra Kumar, IAS, Director General, NIRDPR, presented the notable achievement of the Institute during the past year. He highlighted the key role played by NIRDPR in the Aspirational Block Programme of the NITI Aayog. The DG mentioned documentation of the cases mentioned in Maan ki Baat and setting up of a School of Excellence in Panchayati Raj (SoEPR) among other remarkable achievements of NIRDPR during the last year.
The Director General honoured the Chief Guest with a shawl and presented him with a memento. This was followed by a presentation on the key research findings of the report by Dr C. Kathiresan.
Dr Ravindra S. Gavali, Professor & Head, CNRM, CC & DM, proposed vote of thanks.
The event was attended by faculty members, non-academic staff, students and others.
Online Workshop on Linking CSR with Panchayati Raj (Local Governance) – A Roadmap for Strengthening Private Sector Work in Public Welfare
The Delhi Branch of NIRDPR organised a two-day online workshop on ‘Linking CSR with Panchayati Raj (Local Governance)-A Roadmap for Strengthening Private Sector Work in Public Welfare’, on 28th– 29th November 2023. Around 100 participants from PRIs, CSOs, NGOs and other government autonomous bodies joined the discussion. The programme started with the inaugural address by workshop coordinators Dr Ruchira Bhattacharya, Assistant Professor and Dr Ramesh Sakthivel, Associate Professor, NIRDPR. Dr Sakthivel explained the background of the programme and the expectations from the workshop.

The inaugural lecture of the workshop on ‘Possibilities and pathways to bring CSR directly to the Panchayats’ was taken by Shri S. M. Vijayanand, IAS (Retd.) and President, CRISP. He opined that the Panchayats have such calibre, which can make them better. “There is a need to convince the CSR entities for their participatory involvement and work in the collaborative mode with NGOs for the betterment of Panchayats. Panchayats have enough resources; CSR needs to focus on building the capacity from their funds, which may be done with the help of NGOs and CSR entities. NGOs can be instrumental in the localisation of Panchayats. Panchayats can identify the need-based programmes as they are realistic in planning. Hence, with the help of a participatory approach, village poverty reduction plan can be prepared. CSR funds will be required to fill up the development gaps,” he noted.

Dr. Chandrashekhar Pran, Founder, Teesri Sarkar Abhiyan, discussed the scope of CSR work in the Panchayats from an implementation perspective. He observed that the institutional development of Panchayats is very weak, especially in central India. “Panchayats were established as self-governing bodies where people have the right to take decisions for their betterment and development, but still there is a need for economic development and social justice in the Gram Panchayats. Active participation of villagers is very important as the availability of resources, conditions, etc., vary from place to place, and therefore, one scheme can’t be fruitful for all. Under CSR funding, resources can be planned in a better way. There is a need to focus on the institutional development of Panchayats. CSR funding should be planned at the Gram Panchayat level with the approval of Gram Sabha to bring transparency. Involvements of community need to be included in the CSR proposal as youth and females also matter a lot for proper planning,” he added.
Shri Dilip Pal, Special Secretary RD, Sera Mentor, Sera Trust, focused on the experience of private investments for Panchayat development. He said that the lion’s share of responsibilities of rural development goes to Panchayats as a major part of people’s expectations lies in Panchayats, because of which rural development in India has been happening in the last few decades. He focused on the scope of planning for the comprehensive development of Panchayats. “Very few corporates are ready to work in collaboration with Panchayats and they are also limited to particular streams like health, education and vocational training. Hardly corporates talk about holistic development; there is a need to work on holistic development based on 29 subjects envisaged by the Constitution for the devolution of power to the Panchayats. Corporates and NGOs have highly skilled persons who can prepare quality plan and implement it. Corporates need to work in collaboration with Panchayats so that meaningful transformation can happen in rural areas,” he said.

The second day of the programme started with the case study by Shri Mandeep Singh, District Nodal Officer, Mansa on ‘Experience of Implementing CSR in Panchayats.’ He focused on the need for convergence under MGNREGA and how convergence is increasing the scope and span of work, converging resources, filling gaps and mutually achieving goals. In Mansa district, Bharat Petroleum and Vedanta CSR funds converged under MGNREGA, for which brainstorming exercises and field visits were done for better clarity. Under this project, 83 Anganwadi toilet units, 48 school toilet units, 77 soak pits, 139 ROs, 21 Projectors and 17 sanitary pad vending machines with Incinerators were installed and the project helped in recharging 11,550 litres (an average of 150 litres per school) of water daily & 28,87,500 litres per year. Such activities can be the medium of behavioural change in villages,” he said. Shri Mandeep Singh also presented on works taken up under convergence TSPL CSR funds and convergence with Talwandi Sabo Power Plant Limited under CSR, besides detailing the challenges and benefits achieved through these projects.

Dr. C. Kathiresan, Associate Professor & Head, CIAT & SJ, NIRDPR presented on Localising Sustainable Development Goals (LSDG) and its Integration with Gram Panchayat Development Plan (GPDP) & Evidence-based Planning at Panchayats. He focused on the importance and need of GPDP to strengthen and drive economic development and social justice at GPs. “GPDP needs to be prepared, with the SDGs in view as guiding stars. Localisation of SDGs is a prerequisite for GPDP – the SDGs need to be localised and prioritised in the local context for their attainment through GPDP. Also, GPDP should be evidence-based and data-driven,” he said. Dr Kathiresan also focused on the constitutional provision of planning by stating that the preparation of plan should be for economic development and social justice and in relation to the matters listed in the 29 subjects of the Eleventh Schedule. He briefed the GPDP preparation process, localization of SDGs at Panchayats, preparation of SDG-focused GPDP based on nine themes, and Evidence-Based Planning (EBP) at Panchayats.
Participants raised their queries which were responded to by each resource person, and the programme was very beneficial, according to their feedback. The workshop ended with a vote of thanks.
Watch Day 1 here:
Watch Day 2 here:
5-Day ToT on Agri-Startup/Agri-Entrepreneurship
A five-day Training of Trainers on ‘Agri-Startup/Agri-Entrepreneurship’ was organised at the National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj in Hyderabad from 20th – 24th November 2023. The Centre for Entrepreneurship Development and Financial Inclusion (CEDFI), in collaboration with the Centre for Agrarian Studies (CAS), organised this event.
Addressing the pressing challenges of the agriculture sector, agri-startups and agri-entrepreneurship are rapidly gaining momentum as innovative solutions. These startups leverage technology to boost farm productivity, connect farmers to markets, and fortify food security, playing a pivotal role in reshaping the agriculture sector.
In this dynamic 5-day Training of Trainers (ToT) programme, 24 participants from diverse backgrounds of engineering, agriculture, and food technology, representing the states of Madhya Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Delhi, Punjab, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala and Maharashtra, engaged in a vibrant mix of classroom sessions and enlightening exposure visits.
Key lectures during the programme added substantial depth to the participants’ understanding of agri-entrepreneurship. Dr. Partha Pratim Sahu, Associate Professor & Head of the Centre of Entrepreneurship Development and Financial Inclusion, delivered a comprehensive overview of the scope, opportunities, and challenges in agri-entrepreneurship.
Dr. Ramesh Sakhtival, Associate Professor, Centre for Innovations and Appropriate Technologies for Skills and Jobs (CIATSJ) delved into the activities of Rural Technology Park (RTP), covering various sectors and activities within the park, including agriculture and allied activities, sustainable housing, sustainable energy, food processing, crafts and allied activities, water and sanitation, incubation support, start-up support, and organic and home products.
Additionally, Dr Vanishree Joseph, Assistant Professor, Centre for Gender Studies and Development (CGSD) addressed gender-related prejudices in mainstream contexts. She organised a captivating storytelling activity in Group 4, utilising photographs to vividly illustrate her points.
Prof. Avil Kumar from the Water Technology Centre at Professor Jayashankar Telangana State Agriculture University (PJTSAU) explored Good Agriculture Practices (GAP), shedding light on the history, benefits, and pillars of economic viability, environmental stability, social acceptability, and food safety & quality. His discussions extended to GAP for multiple crops, including rice, millet, soybean, vegetables, fruits, and medicinal crops.
Dr. Saravanan Raj, CEO, Centre for Innovation and Agripreneurship, National Institute of Agricultural Extension Management (MANAGE), Hyderabad, outlined the centre’s programmes and offerings to promote entrepreneurship in agriculture. He also highlighted the various startups collaborating with MANAGE.

Mr. Jonathan Philoy, Director of Food and Agriculture at the Research & Innovation Circle of Hyderabad (RICH), shared insights into collaborative projects promoting agritech startups throughout the agri value chain.

Mr. Purushotham Rudraraju, Manager of Agribusiness at ICRISAT, spoke on the topic ‘Agripreneurship Excellence: Cultivating Innovation in Agriculture.’ He discussed innovation, and its characteristics and forms. He delved into agribusiness opportunities in India, emphasising its advantages in the startup ecosystem. He also provided illustrations of agri value-added products in fruits and vegetables.
Dr Surjit Vikraman, Associate Professor and Head of the Centre of Agrarian Studies (CAS), provided valuable insights into the value chain in agriculture, differentiating between supply chain and value chain, highlighting the need for a value chain, and highlighting innovative interventions by startups.
Dr Jyothi Prakash Mohanty from NRLM – Resource Cell elucidated marketing interventions for promoting agripreneurship by OLM and ORMAS. His discussion encompassed multiple marketing activities for products manufactured by SHG women, spanning processing units for jaggery, mango, handloom, sabai grass, etc.
Mr Surajit Sikdar, Assistant Director, Skill Innovation Hub, DDUGKY engaged participants in a case discussion, unravelling skilling strategies toward agripreneurship.
Dr P. P. Sahu took a comprehensive session on multiple schemes and programmes aimed at promoting agriculture and agripreneurship, leaving participants equipped with a wealth of knowledge and inspiration to drive innovation in the agriculture sector.
Classroom sessions were supplemented by field visits. Under expert guidance, the visit to the Rural Technology Park (RTP) became a gateway to understanding diverse models of sustainable livelihood. RTP emerged as a platform for technology demonstration, dissemination and transfer, showcasing innovations in green energy solutions, water and sanitation technologies, and both farm and non-farm activities. The National Rural Building Centre (NRBC) took the centre stage, demonstrating models of sustainable and cost-effective housing that captured the cohort’s attention.
The year 2023 being declared as the International Year of Millets, the participants had the privilege of visiting the Indian Institute of Millet Research in Hyderabad. Scientists from the institute outlined its objectives, engaging participants in discussions on various types of millets, their usage, and nutritional benefits. The visit included a walkthrough of the centre of excellence on value addition of millets, where Nutri-Hub’s various value-added products were showcased. Participants also explored the manufacturing unit and the institute’s field area, gaining insights into millet production and value-added product nuances.
The last session ended with a wealth of peer learning, and experiences and initiatives from states, all marked by a rich infusion of creativity and inclusivity. These experiences were generously shared by individuals working at the grassroots level with communities. They offered valuable insights into real-life problems, the challenges faced, and, most importantly, strategies for overcoming these challenges. Participants also submitted online feedback on the Training Management Portal (TMP).
This 5-day ToT was jointly conducted by Dr Partha Pratim Sahu (Centre for Entrepreneurship Development & Financial Inclusion) and Dr Surjit Vikraman (Centre for Agrarian Studies).
(Note: This report is prepared by participants Ms Aarti Pathak and Mr Mayank Sahu with inputs from Dr. Partha Pratim Sahu)
Capacity Building of PRIs for Strengthening Community Health Care with a Focus on LSDG Theme 2: Healthy Village

The National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj organised a four-day training programme on enhancing the capacity of Panchayati Raj functionaries in the implementation of community health programmes on its Hyderabad campus from 14th to 17th November 2023. Nearly 40 participants from different states, representing various line departments, NGOs, and academia, attended this four-day programme. The programme centred around the targets and indicators outlined in Theme 2 of the Localisation of Sustainable Development Goals, specifically addressing the creation of Healthy Villages.
Dr Sucharita Pujari, Assistant Professor at CPGS&DE, NIRDPR and Programme Coordinator commenced the sessions by providing an overview of the health and wellness indicators of the Localisation of Sustainable Development Goals. She delved into the targets set, followed by an in-depth presentation on the Social Determinants of Health, stressing the multifaceted nature of health.
The training programme placed a strong emphasis on key sessions that addressed crucial topics such as Behaviour Change Interventions for improved health outcomes, the Role of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) in achieving Universal Health Coverage, Social Accountability for better MCH outcomes and the important role of PRIs, and discussions on Best Practices and Community Health Care Management Initiatives, with a specific focus on the increasing role of PRIs in community mobilisation and awareness generation on health.

Dr Vandana Prasad from the National Health Systems Resource Centre, New Delhi, in her presentation on ‘Universal Health Coverage and the Role of Local Governance, centred on comprehensive primary healthcare through Ayushman Bharat Health Wellness Centres for community health development. She emphasised the need for rural local bodies to be involved in planning, monitoring, and taking necessary actions to improve health facilities in their jurisdictions. Furthermore, she highlighted the increasing role of Gram Panchayats in implementing the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya (PMJAY) scheme in rural India in line with LSDGs.
Ms. Poornima from Karnataka Health Promotion Trust discussed social accountability tools, underlining the critical role of PRIs for better MNCH outcomes. Ms. Renukapoor from FPA, Hyderabad, led a session on Sexual and Reproductive Health (SRH), an emerging concern impacting women’s health, and discussed strategies to address it.
A session on ‘Community Health Initiatives Based on the West Bengal Experience’ was conducted by Shri Dilip Ghosh, Former Secretary, Department of Rural Development and Health and Family Welfare, Government of West Bengal. He took the participants through the Community Health Care Management Initiative programme in West Bengal, focusing on building the capacity of Panchayat bodies in health and the processes involved.
These sessions highlighted the pivotal role of PRIs in the effective implementation of health programmes within communities, underscoring their significance in driving positive health-related outcomes.
Capacity Building and Experience Sharing Workshop on Community Adaptability and Sustenance Mechanisms at the Intersectionality of Water and Climate Change
The Delhi Branch of NIRDPR has partnered with the Sehgal Foundation for a series of workshops on ‘Community Adaptability and Sustenance Mechanisms at the Intersectionality of Water and Climate Change’ with funding support from DCB bank.

The inception workshop of the series titled ‘Jalagam’ on Community Adaptability and Sustenance Mechanisms at the intersectionality of Water and Climate Change was conducted at the Ashok Hotel, New Delhi, on 30th November 2023. More than 100 participants from various think tanks, NGOs, CSOs, and research bodies across India joined the workshop.
The workshop started with a welcome note by Ms Niti Saxena, Sehgal Foundation, followed by opening remarks of Dr Anjali Makhija, CEO of Sehgal Foundation. The workshop was graced by Smt Vini Mahajan, Secretary, Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Ministry of Jal Shakti; Shri Ashok Goel, Commissioner, Ministry of Jal Shakti; and trustees of S M Sehgal Foundation Smt. Neelima Khetan and Dr Suhas P. Wani; and Mr. Avinash Mishra, former member of NITI Aayog.

The workshop constituted of three panels featuring discussions around community adaptability and sustenance mechanisms in addressing water-related challenges.
The first panel discussion was based on ‘Achieving 2030 SDG Agenda: Converging Policies and Innovations’ moderated by Dr Suhas P. Wani (International Advisor to ADB, IFAD, FAO) with Mr Mohammad Faiz Alam (International Water Management Institute), Mr Nitin Bassi (Council on Energy, Environment and Water) and Dr Pallavi Kumar (Johns Hopkins Program for International Education in Gynaecology and Obstetrics) as panellists.
The second panel on ‘Driving Water Security in Rural India: Stakeholder Perspective’ was moderated by Mr Salahuddin Saiphy (S M Sehgal Foundation) with Mr Robin Singh (CLUIX Private Limited) and Mr Aswin Kumar D (Dalmia Bharat Foundation) as panellists.
The third panel on ‘Championing Community Resilience: Voices of Rural India’ was moderated by Ms Neelima Khetan (Trustee, S M Sehgal Foundation) with Dr Ruchira Bhattacharya (NIRDPR), Mr Asad Abbas (Aga Khan Foundation) and Ms Aakriti (Development Alternatives) as panellists. Dr Ruchira Bhattacharya spoke on the critical role of intermediary bodies to achieve community ownership and action for sustainable development goals.

In the final session, describing the value of ‘Contribute to Society’ at DCB Bank and its impact, Mr Murali M. Natrajan, Managing Director and CEO of DCB Bank, shared how micro efforts and large ideas could bring in changes. “The relation between water and waste management affects the overall health and water of a nation. The Bank’s CSR projects and activities mainly focus on water crisis, climate change, sustainable livelihoods & preferably Nature-Based Solutions (NBS),” he added.
The workshop witnessed enthusiastic participation from the participants who shared their experiences in the field of water resources and garbage management and brought out the best practices across regions in the states of Delhi, Maharashtra, Telangana, and Uttar Pradesh. The workshop ended with the promise of fostering collaboration and partnership for sustainable water security in the face of climate change.
Observance of Vigilance Awareness Week – 2023 at NIRDPR
The National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj observed Vigilance Awareness Week from 30th October 2023 to 5th November 2023. As per the Central Vigilance Commission guidelines, the theme for the year was “Say no to corruption; commit to the Nation”.
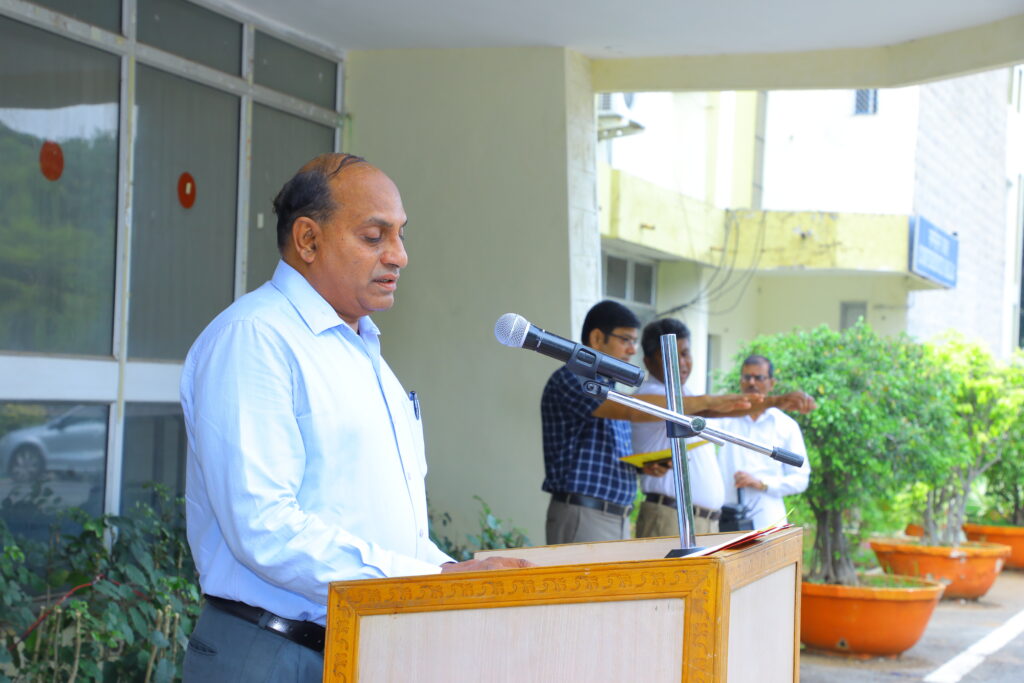

The observance of Vigilance Awareness Week at the Institute commenced with the integrity pledge taking ceremony in front of Dr B. R. Ambedkar Block on the campus on 30th October 2023. The programme began with the introductory note of Dr R Ramesh, Associate Professor & Chief Vigilance Officer, followed by the CVO reading out the message from the President of India on Vigilance Awareness. Dr G. Narendra Kumar, IAS Director General, NIRDPR administered integrity pledge to the faculty members, and staff of NIRDPR.
An essay competition on vigilance themes was held on 1st November 2023. Faculty and employees participated in the competition organised on the topic ‘Can market-creating innovations be a critical catalyst for people ‘not having to choose (hire)’ corruption?’
Shri Dharmendra Singh, Computer Programming Associate secured first position and Shri G. Praveen, Data Processing Assistant got second position. Dr Vanishree Joseph, Assistant Professor, CGSD and Dr Lakhan Singh, Assistant Professor, CHRD, evaluated the essays.
A quiz competition was organised on 02nd November 2023 based on the topics of preventive vigilance, Central Civil Service (CCS) Rules, government schemes, government apps, general knowledge, etc.
In total, four teams participated, and the team comprising Shri Dharmendra Singh, Ms K. Gayathri Prabha, Smt. S.V. Lakshmi and Shri M. D. Ubed got the first position. The team comprising Shri Karthik Krishna, Shri V. Srikanth, Smt. Y Prameela and Shri Sunil Kumar Jha secured the second place.
The valedictory session of Vigilance Awareness Week was held at Vikas Auditorium on 9th November 2023. Dr R. Ramesh, Associate Professor & CVO, delivered the welcome address. In his opening remarks, Dr G. Narendra Kumar, IAS, Director General, NIRDPR, emphasised the importance of honesty and integrity with examples. The DG also emphasised the hierarchy of vigilance – starting from simple compliance to honesty to integrity to effectiveness in service delivery.

A talk on ‘Integrity in Public Service’ was delivered by Dr I. V. Subba Rao, IAS, former Secretary to the former Vice President of India. He quoted Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel’s guiding vision for civil service. “Every year Vigilance Awareness Week starts from the birth anniversary of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel. He is remembered as the patron saint of India’s civil servants for playing a pioneering role in establishing the modern All India Service System,” he said.
“Government servants should maintain utmost impartiality and incorruptibility of administration. The paradigm shift from Swaraj (self-government) to Surajya (good governance) denotes that governments should be sensitive towards the common man and weaker sections. One needs to give importance to accountability and transparency in public service,” he added.
Dr I. V. Subba Rao and Dr G. Narendra Kumar distributed the prizes to winners and participants. The programme concluded with vote of thanks by Dr R. Ramesh.
(This report is prepared by Mr Samuel Varghese, Research Officer, Vigilance Cell, NIRDPR, Hyderabad)
Writeshop on Development of Training Module on Health under the Aspirational Block Development Programme
The National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR) organised a two-day writeshop from 21st – 22nd November 2023, on its campus in Hyderabad, to develop a comprehensive training module on health for block-level officials under the Aspirational Block Programme (ABP) of the Government of India. The writeshop brought together public health experts, practitioners, officials from NGOs and academia to deliberate and collaboratively contribute to the design and formulation of the training module. Their diverse expertise and practical insights added significant value to the module development process.
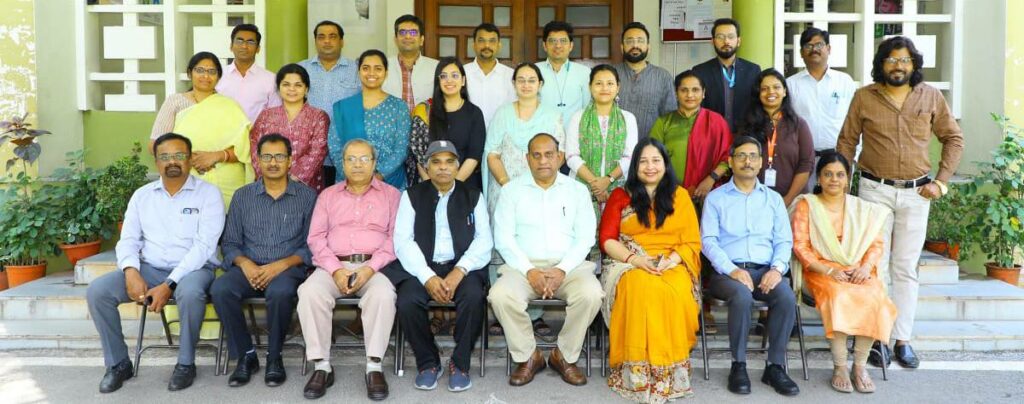

The workshop began with an inaugural address by Dr G. Narendra Kumar, IAS, Director General, NIRDPR, who emphasised the pivotal role of the Aspirational Block Programme in improving the quality of lives of rural people. He underscored the need for a concerted effort to identify health challenges and prioritise interventions in aspirational blocks. The Director General clearly outlined the priorities by focusing on identifying bottlenecks in health programme implementation, establishing linkages with Gram Panchayat Development Plans, showcasing best practices, and formulating strategic plans for overcoming challenges in Social and Behaviour Change Communication (SBCC), Monitoring, and Evaluation.
The workshop featured thematic discussions, group exercises, and presentations to facilitate brainstorming and knowledge sharing. A significant portion of the writeshop was dedicated to group work, where participants collaborated on designing the curriculum for the health training module.
The two-day writeshop concluded with a note of gratitude extended by Dr Sucharita Pujari, Assistant Professor at CPGS&DE, NIRDPR and the coordinator of the event, thanking participants for their valuable contributions, suggestions, and feedback. The module, once finalised, will serve as a valuable resource for training block-level officials involved in the implementation of health programmes at the grassroots level.
NIRDPR Delhi Branch Organises Six Workshops at SARAS Aajeevika Mela in Gurugram
The Centre for Marketing & Promotion of Rural Products, Entrepreneurship Development (CMPRPED), NIRDPR Delhi Branch organised a series of six workshops during SARAS Aajeevika Mela on behalf of the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD). The mela was organised from 26th October to 11th November 2023 at Leisure Valley Park in Gurugram, Haryana.
Workshop on ‘Creating a Reputable Brand for Rural Products: Better Designing and Packaging’ on 30th October 2023
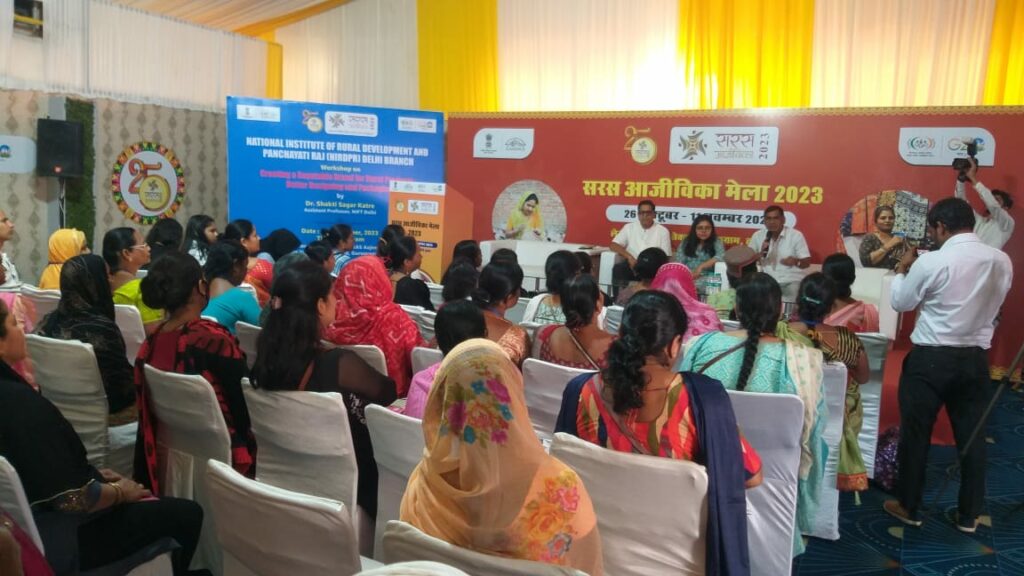

A workshop on ‘Creating a Reputable Brand for Rural Products: Better Designing and Packaging’ was conducted at the conference hall of the SARAS Aajeevika Mela in Leisure Valley Park Ground, Gurugram on 30th October 2023, in which 101 SHG women participated.
Dr Shakti Sagar Katre Assistant Professor, NIFT, Delhi was the keynote speaker of the workshop. Dr Ruchira Bhattacharya, Assistant Professor, NIRDPR introduced the participants and briefed them about the objectives of the workshop for promoting SHGs’ business. Shri Chiranji Lal, Assistant Director, NIRDPR briefed how the sales could be increased with the help of good packaging and display of the products.
Dr Shakti Sagar Katre made a presentation on the importance of the brand with the help of examples and interactions with the participants. He said that most of the products, which are used in our daily lives, are recognised by their brand. “Every product has the quality to convert itself into a brand. The first brand may be created at the local level and may be spread gradually by involving more people. Experience, emotions with the products, relationship with the customers and attached stories are also important for branding. When it comes to branding, the visual identity of the product is a crucial element and it should not be changed frequently. While designing the products, it should be attached with some personality. Social messaging may also be conveyed through widely acceptable products. Before creating a brand, a team or group should have the learning capability, integrity, values to the customers, team spirit and ownership. Products should have some innovative qualities, and they should be designed according to the aesthetic understanding of the buyer,” he said.
“Visibility and accessibility to the products attract the buyer; hence, the display of the products is a very important aspect for maximising sales. Display of the products is a reason that attracts buyers at the malls; this may also be introduced in the stalls too. With the help of smart ideas, display at the stall may be arranged attractively. Packaging does not require a big investment; attractive packaging can be done with the help of small tools and techniques, items like bamboo sticks, cartons, yarns of bananas, paper folding, etc.,” he added.
Workshop on ‘Sale Communication Strategy with Buyer’ on 2nd November 2023

A workshop on ‘Sale Communication Strategy with Buyer’ was conducted at the conference hall of the Saras Aajeevika Mela at Leisure Valley Park Ground, Gurugram on 2nd November 2023, in which 102 SHG women participated. Dr Sangeeta Pranvendra, Professor at the Indian Institute of Mass Communication was the main speaker. Dr Ruchira Bhattacharya Assistant Professor, NIRDPR introduced the participants and briefed them about the objectives of the workshop. Shri Chiranji Lal, Assistant Director, NIRDPR was also present during the workshop.
Dr Sangeeta Pranvendra spoke about how women could contribute towards the progress of the country. She briefed about the media strategies for promoting the sale of rural products. “The SHG members should learn promotion of rural products through
social media without investing money. Digital communication is one of the important platforms, which may give sufficient power to woman to promote their products. Initially, the women can share ideas through WhatsApp Groups. Thereafter, they may open Facebook & YouTube accounts, etc., where they can upload videos of their products. Digital platforms may be very useful for rural women, as they save time and money and can be accessed from anywhere. Women SHGs can create the profile of their groups on Facebook through their mobile and can create a bond with the buyer. Every rural product has a particular lifecycle involving different stages like development of products, introduction to the market, stages of profit and maturity. At the last stage of declination, SHGs need to think about introducing new & updated products,” she said.
“Generally, rural products lack branding and advertising. Hence, social media may be an important platform for the promotion of rural products and marketing them. For this, women SHG members have to learn about the planning to promote their products online. They should understand the taste of customers and the needs of the market. Online communication with buyers can be made through websites, social media, apps, e-commerce portals, etc. To sell the product online, the shape and size of the products should be designed accordingly so that courier charges may be reduced, and packaging may be done properly. For online marketing, online payment and transactions should be checked and monitored regularly. Before going to bigger platforms like Myntra and Amazon, bulk quantities of products should be available with the group to avoid the situation of stock out. Excess of the stock may be sold in the form of sales. SHGs will have to focus on media engagement practices and plan to identify the needs of the market to sell the product. They need to learn about the online payment protocol to avoid fraud,” Dr Sangeeta added. Dr Ruchira Bhattacharya concluded the session.
Workshop on ‘Business Development Strategy’ on 3rd November 2023
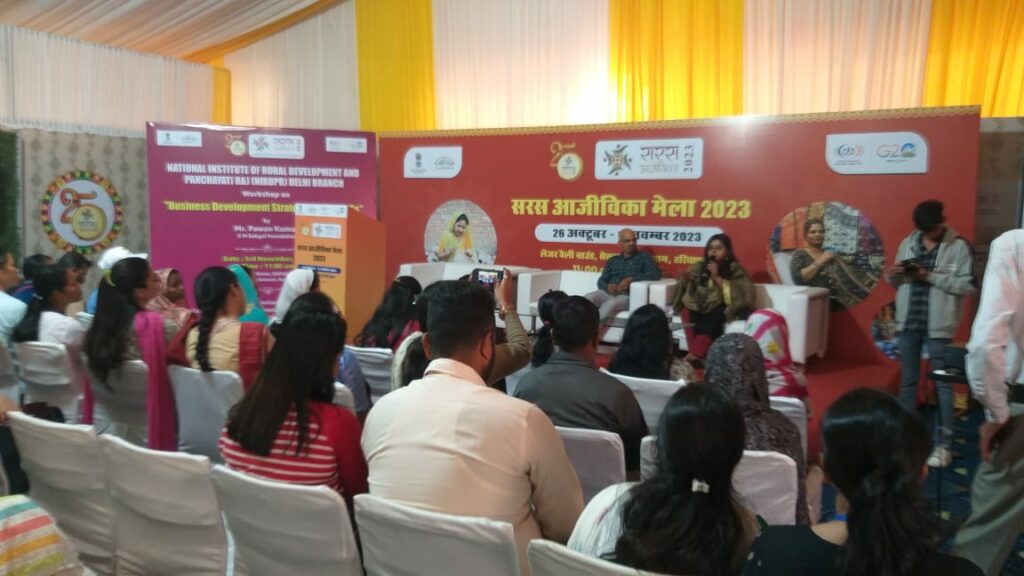

The third workshop on ‘Business Development Strategy’ was organised at the Conference Hall of the SARAS Aajeevika Mela at Leisure Valley Park Ground, Gurugram on 3rd November 2023, in which 96 SHG women entrepreneurs participated.
Mr Pawan Kumar from the S. M. Sehgal Foundation was invited as the keynote speaker. The workshop started with a welcome address by Dr Ruchira Bhattacharya. She briefed the participants about the setting up of the business and its promotion. Shri Pawan presented business development strategies and opined that despite performing well in their groups, women need a bit of improvement. “Economic empowerment is very important for women. There is a need for training to set up a business, through which women can understand production technology, access to raw materials, financial planning, demand for the product, and cost-benefit analysis. For business development leadership quality is necessary. Women should be aware of the market, from where they can get the raw material and loans at lower rates,” he noted.
“By incorporating some innovative ideas into the local products, sales can be promoted. Proper training for women can enhance their skills in learning about the needs of the market and cost analysis. There are various institutions like KVK which impart training to women on innovative ideas and proper planning for setting up a business,” he added. Dr Ruchira Bhattacharya concluded the session.
Workshop on ‘Promotion and Marketing of Rural Products through Social Media’ on 06th November 2023

A workshop on ‘Promotion and Marketing of Rural products through Social Media’ was conducted at the Conference hall of the SARAS Aajeevika Mela at Leisure Valley Park Ground, Gurugram on 6th November 2023, in which 69 participants participated.
Shri Vinod Sharma from the Indian Institute of Mass Communication was invited as the main speaker. The workshop started with a welcome address by Shri Chiranji Lal, Assistant Director (Marketing). He briefed the participants about the objective of the session. Shri Vinod Sharma spoke to the participants about using mobile as an important tool for promoting their business through social media. He said that a saree that is picked up from the rural artisans at Rs.1000 is being sold for more than Rs.2500, and therefore, the SHGs must promote their products online to get more profit.
“As far as the promotion of a product is concerned, the online presentation should be decent. Buyers are attracted to the products that look good. A brief description of the product is also very important. Best keywords and hashtags should be used so that products can easily be searched on the search engine,” he said. While interacting with the artisans, he demonstrated how a Facebook page is created, besides detailing the shooting of video footage, look of the thumbnail and background music of the video. He also focused on the importance of colour contrast of the page and providing the contact details of the seller. Shri Vinod Sharma also visited a few stalls to give demos on shooting videos and explain the effects of light during photoshoots.
Workshop on ‘Startup by Self Help Groups (SHGs)’ on 07th November 2023

A workshop on ‘Startup by Self Help Groups (SHGs) was conducted at the Conference Hall of the SARAS Aajeevika Mela, Leisure Valley Park Ground, Gurugram on 7th November 2023. In total, 87 participants, including SHG members and state Coordinators participated. A team of Startup India from the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Govt. of India took the session. The workshop started with a welcome address by Dr Ruchira Bhattacharya, Centre Head NIRDPR, Delhi Branch, who introduced the participants to the main objectives of the workshop. Shri Chiranji Lal, Assistant Director, NIRDPR Delhi Branch, briefed the participants about the purpose of the workshops. Shri Rajeev Singhal, National Mission Manager, NRLM briefed how SHGs can learn from the team of Startup India and can implement the same in their business to promote their business to get more success.

Ms Pallavi Gupta and Shri Neeraj Gupta from the team of DPIIT explained to the participants the purpose of Start-up India and how funding and industrial partnerships could be created through the Start-up India website. Shri Akhil Gupta from Mazout Electric Pvt. Ltd. shared about his journey of becoming an entrepreneur. “For any startup, the customer’s problem should be identified, followed by a market study, fixing an advisor, and doing the basic work. For starting a venture, a proper team, proof of concept videos and a business model are also important. A support system is also required which may provide support in the legal aspects and other matters,” he added.
Shri Naveen Yadav, Principal HR Advisor, Grey Beez Private Limited presented on the significance of proper mentorship and guidance. Manik Sehgal from RAASA briefed the participants about his journey and the importance of digital marketing.
Workshop on ‘Business to Business (B2B) Meeting’ on 08th November 2023

A workshop on Business to Business (B2B) Meeting was conducted at the Conference Hall of the SARAS Aajeevika Mela at Leisure Valley Park Ground, Gurugram on 8th November 2023, in which 81 Participants (SHGs and State Coordinators) participated. Representatives from ONDC, Amazon, SignCatch, etc., were invited to brief the participants about selling the products on various online platforms. The workshop started with a welcome address by Shri Chiranji Lal, Assistant Director, NIRDPR Delhi Branch.
Shri Avinash Kumar Choudhry from ONDC focused on the importance of online platforms. He briefed how ONDC technically connects the buyer and seller application and logistic support to promote the business. With the help of KYC, GSTIN and catalogue, the seller can easily create their profile on the ONDC and sell their products as they do in their day-to-day life.
Shri Shailendra from Amazon briefed about the importance of Amazon Karigar and Amazon Saheli platforms of Amazon, which are, respectively, designed for artisans and women. Stating that Amazon has more than 10 lakh sellers, he also briefed the safety claim policy for the sellers, the importance of quality products and the creation of the catalogue.
Shri Nitin Gupta, Head of Sales from SignCatch briefed how participants can create their account on ONDC without maintaining multiple e-commerce profiles by defining their area of visibility. He also distributed the brochure to the participants to create their profiles.
All queries raised by the participants were answered by the resource persons who handled various sessions. Participants appreciated the workshop and found all sessions beneficial.

